This page provides information on V-Ray Omni Light or Point Light.
Overview
V-Ray Omni Light is a V-Ray specific light source plugin that can be used to create physically accurate area lights. It emits light in all directions from a single source. The Omni Light can be used to simulate point source lights.
UI Paths
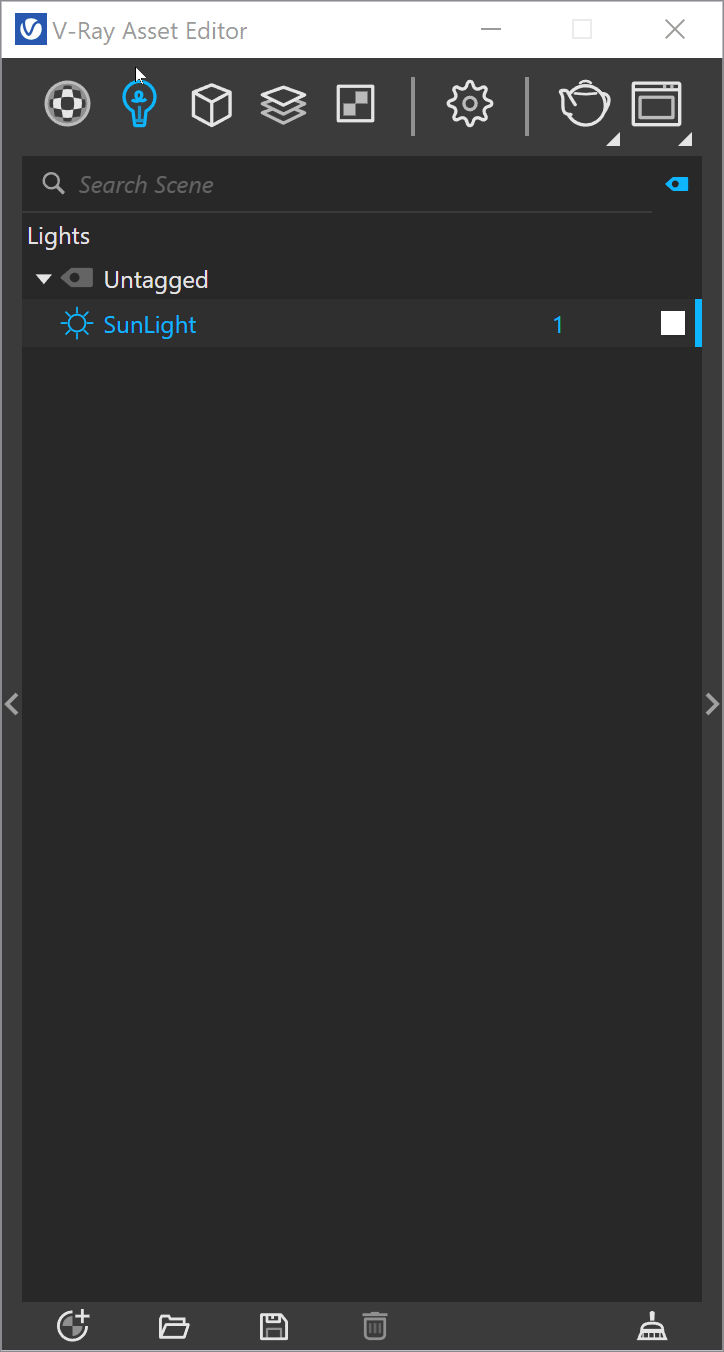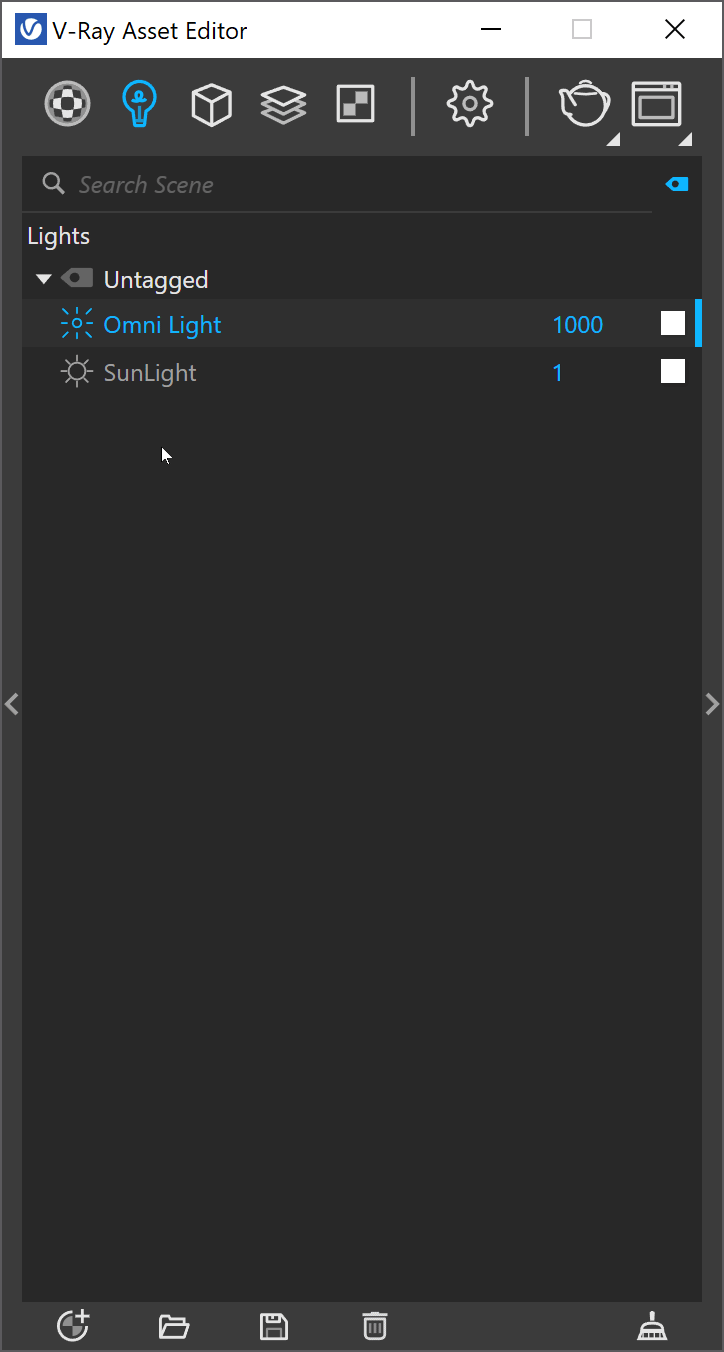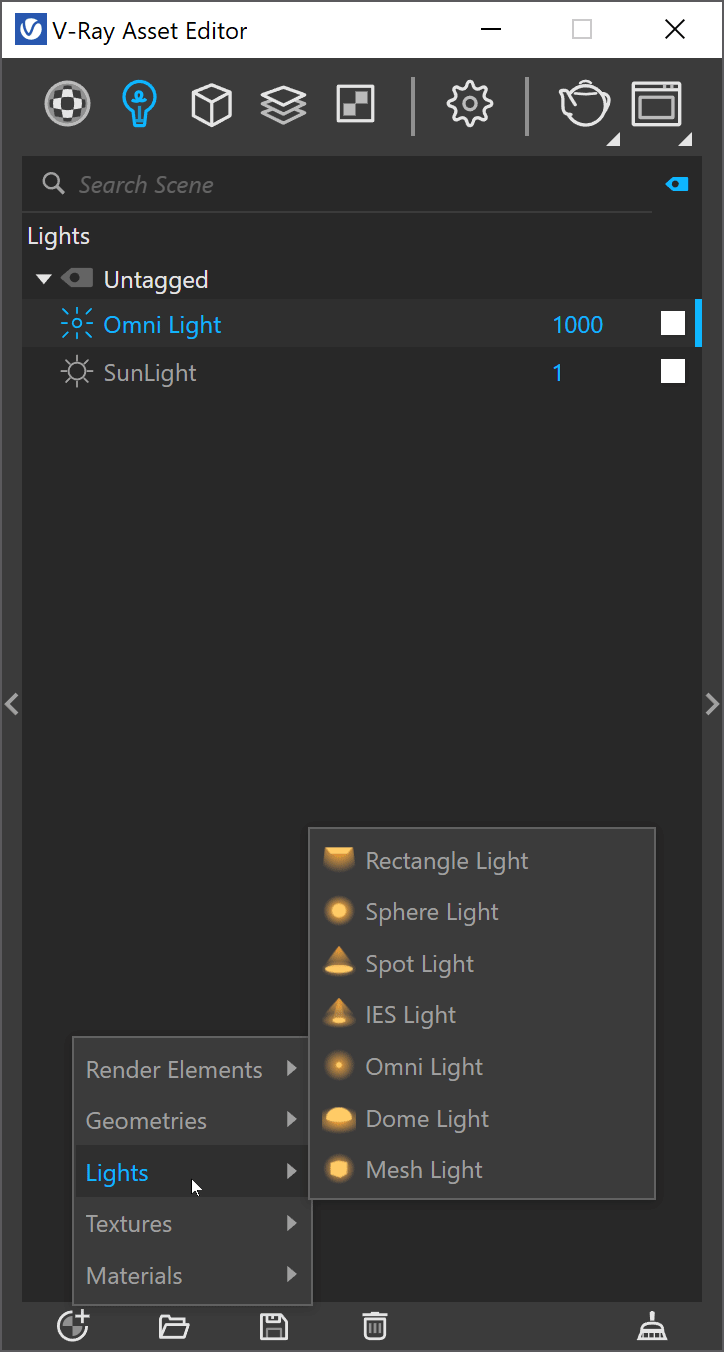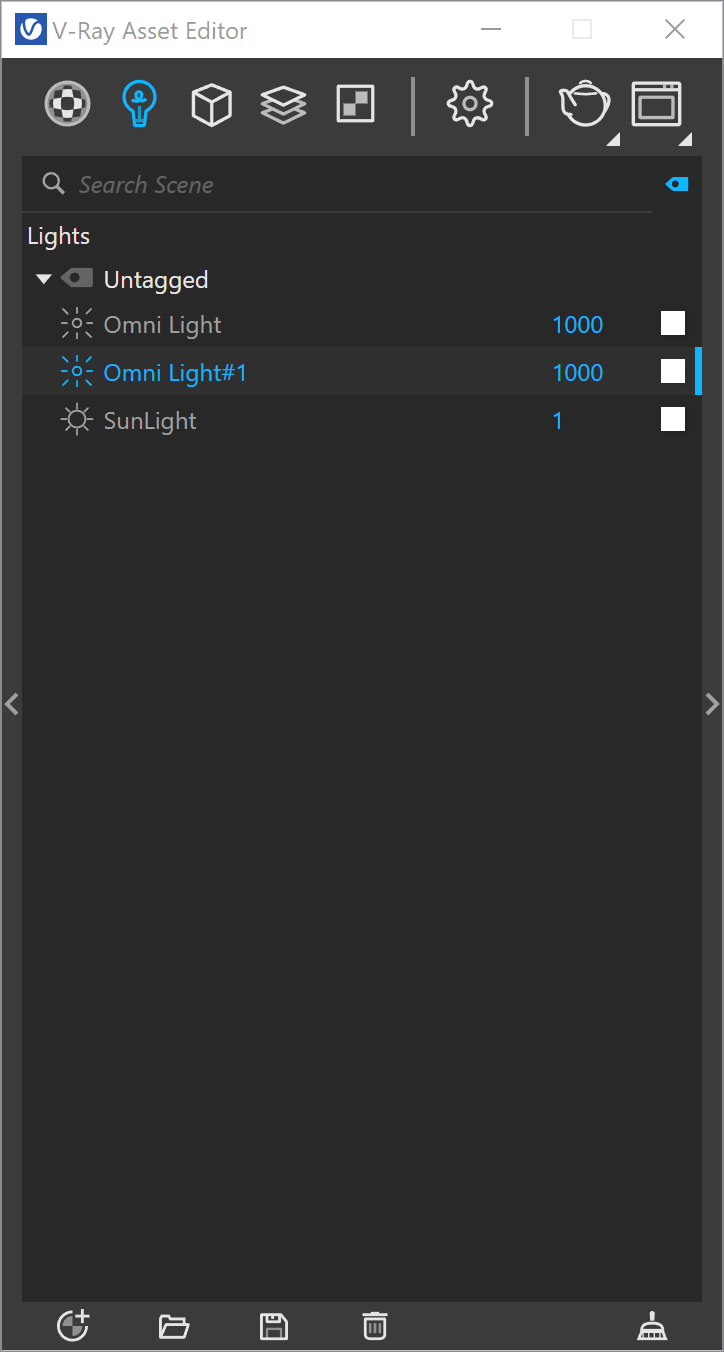
||V-Ray Asset Editor|| > Lights (right-click) > Omni Light
||V-Ray Asset Editor|| > Create Asset (left-click) > Lights > Omni Light
||V-Ray Lights Toolbar|| > Omni Light
SketchUp Menus Ribbon
||Extensions|| > V-Ray > Lights > Omni Light
Parameters
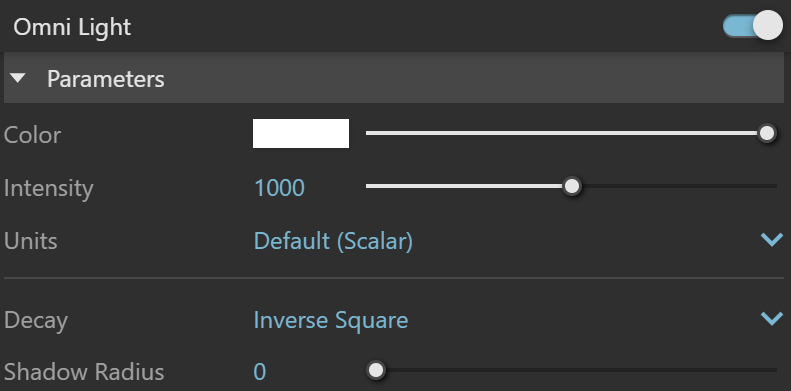
Enabled () – Turns V-Ray Omni Light on and off.
Color – Specifies the color of the light when the mode parameter is set to Color. When using photometric units, this color is normalized, so that only the color hue is used, and the light intensity is determined by the Intensity parameter.
Intensity – Specifies the strength of the light. See Intensity example below for comparison.
Units – Specifies the light unit of measurement. Using correct units is essential when working with physical camera exposure. The light automatically takes the scene units scale into consideration to produce correct result.
Default (Scalar) – The color and multiplier directly determine the visible color of the light without any conversion. The light surface will appear with the given color in the final image when seen directly by the camera.
Luminous Power (Lumens) – Total emitted visible light power measured in lumens. The intensity of the light will not depend on its size. A typical 100W incandescent light bulb emits about 1500 lumens of light.
Luminance (lm/m^2/sr) – Visible light surface power measured in lumens per square meter per steradian. The intensity of the light depends on its size.
Radiant Power (W) – Total emitted visible light power measured in watts. The intensity of the light does not depend on its size. This is not the same as the electric power consumed by a light bulb for example. A typical 100W light bulb only emits between 2 and 3 watts as visible light.
Radiance (W/m^2/sr) – Visible light surface power measured in watts per square meter per steradian. The intensity of the light depends on its size.
Decay – Sets the behavior of the light intensity from the distance of the light source. Тhe light intensity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the light (surfaces that are farther from the light are darker than surfaces which are closer to the light).
No Decay – Light intensity will not decay with distance.
Inverse – Light intensity is inversely proportional to the distance from the light.
Inverse Square – Light intensity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the light. This is the normal behavior of light.
Inverse Cube – Light intensity is inversely proportional to the cube of the distance from the light.
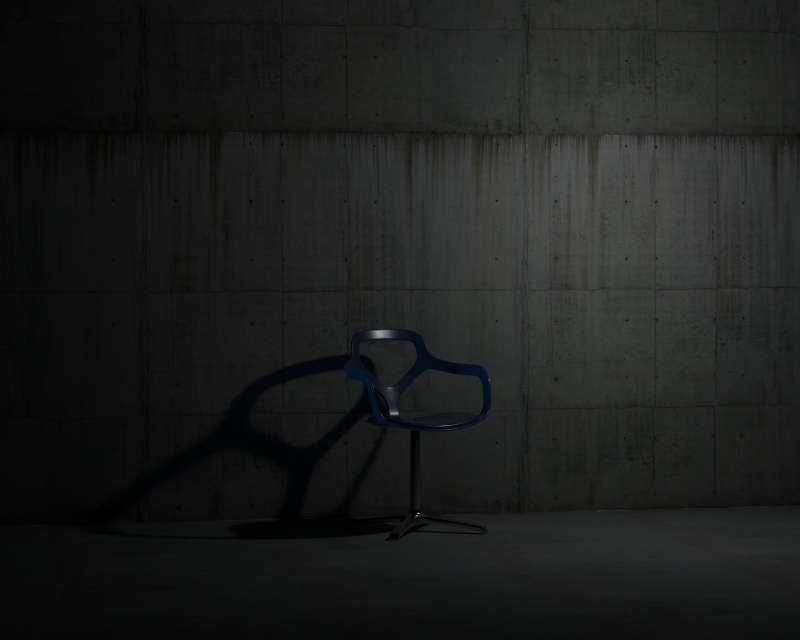
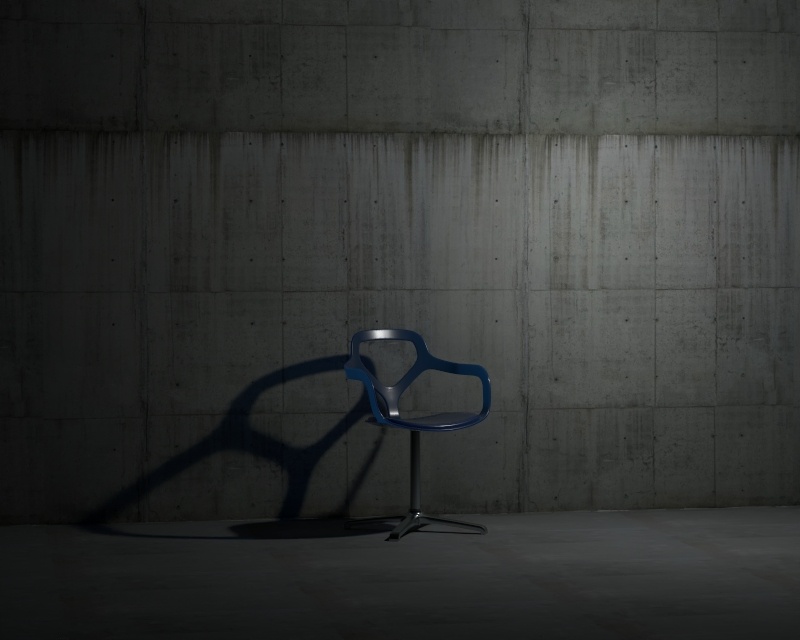
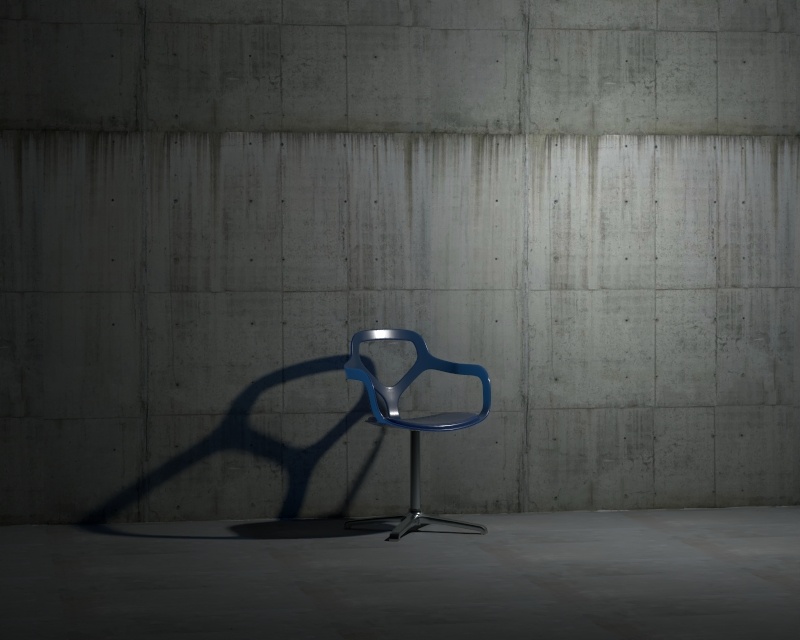
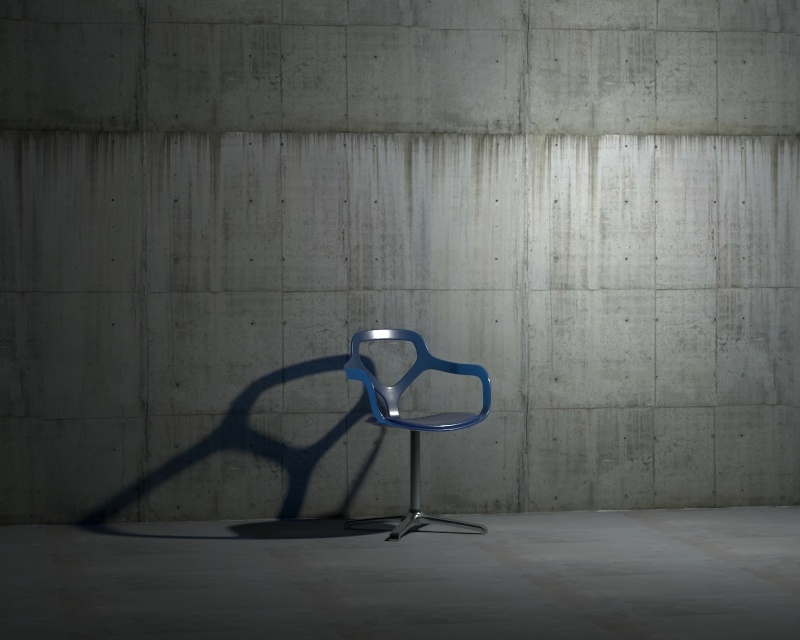
Shadow Radius – Controls the size of the light. Where 0.0 is a point light, larger values produces soft (area) shadows. See Shadow Radius example below for illustration.
Options
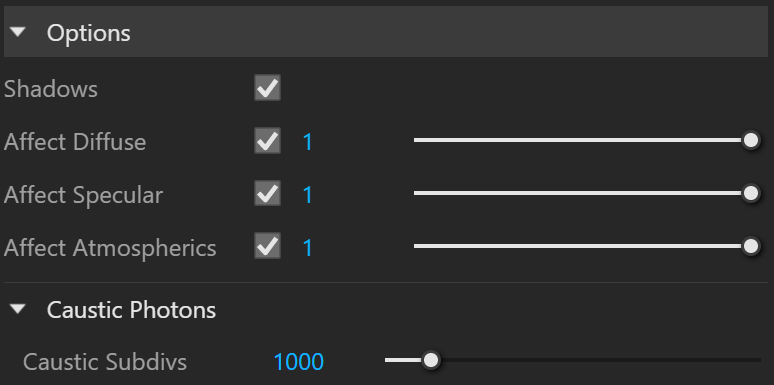
Shadows – When enabled (default), the light casts shadows. When disabled, the light does not cast shadows.
Affect Diffuse – Determines whether the light is affecting the diffuse properties of the materials. With this option off, there is no diffuse contribution from the light.
Affect Specular – Determines whether the light is affecting the specular of the materials (i.e. glossy reflections). With this option off, there will be no specular contribution from the light.
Affect Atmospherics – Specifies whether the light influences the atmospheric effects in the scene. The value determines the amount of involvement.
Caustic Subdivs – Controls the amount of photons that V-Ray traces to estimate caustics. Large numbers slow down the calculation of the caustics photon map and may take more memory.
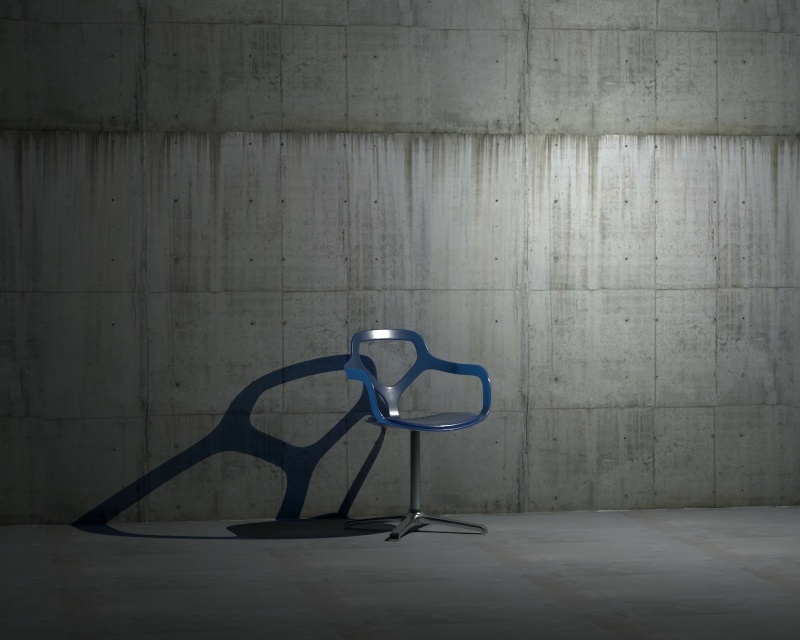
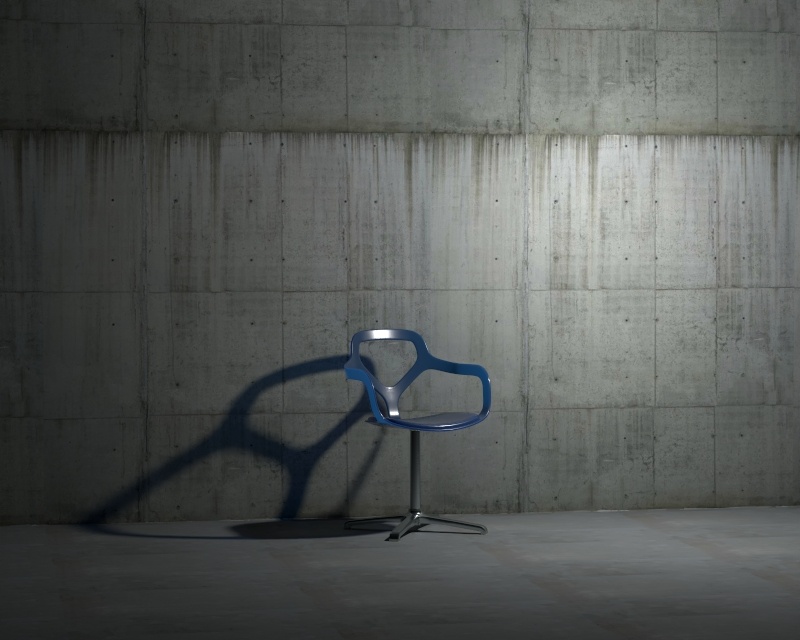
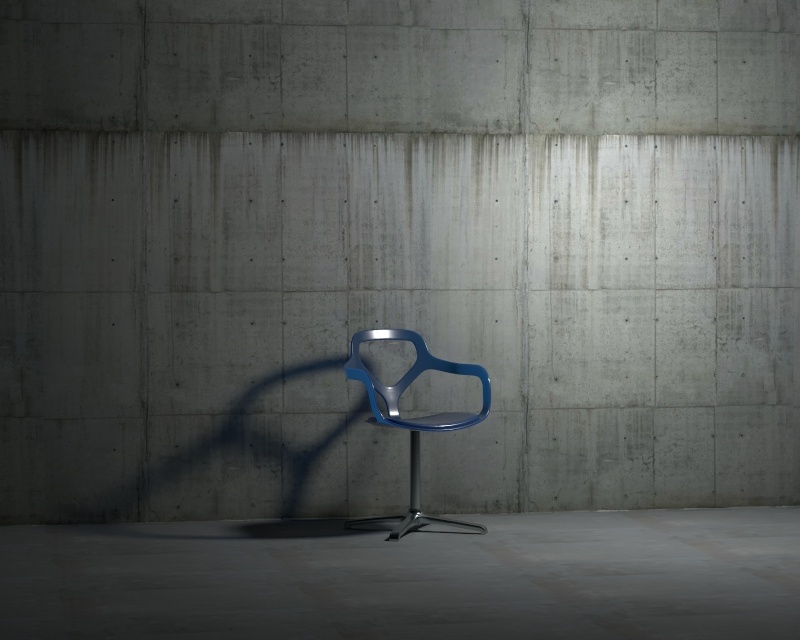
Example: Intensity
This example shows how changing the Intensity parameter changes the light in the scene. Note that the values are calculated as Lumens.
Example: Shadow Radius
This example shows how the Shadow Radius parameter affects the light in the scene. Notice how lesser values result in sharper shadows and greater values result in blurrier and elongated shadows.
Notes
- Scene units in SketchUp are always calculated in inches.