This page provides information about the Noise (Simplex) texture in V-Ray for Blender.
Overview
The Noise Simplex texture creates a Simplex procedural noise. Simplex noise is a method developed by Ken Perlin as a more efficient alternative to Perlin Noise. One of the main advantages of Simplex Noise over Perlin Noise is its scalability to higher dimensions while retaining speed and quality. See the Reference section for the full paper on Simplex Noise.
UI Path
||Node Editor|| > Add > Textures > Noise (Simplex)
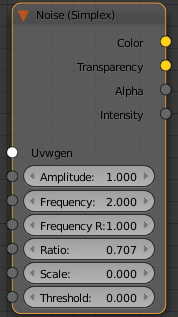
Node
Amplitude – Controls the amount of distortion in the noise. A value of 0 make these a straight line.
Frequency – Controls the the amount of Noise generated. Higher values create smaller, finer noise.
Frequency Ratio – Controls the amplitude ratio between two consecutive levels of the fractal noise. A value of 0 makes only the first noise level affect the result, and a value of 1 makes all noise levels affect the result with the same weight.
Ratio – Controls the fractal noise frequency.
Scale – Controls the translation for the noise UVW coordinates.
Threshold – Threshold value for the noise. Clamps all values going beyond the specified one.
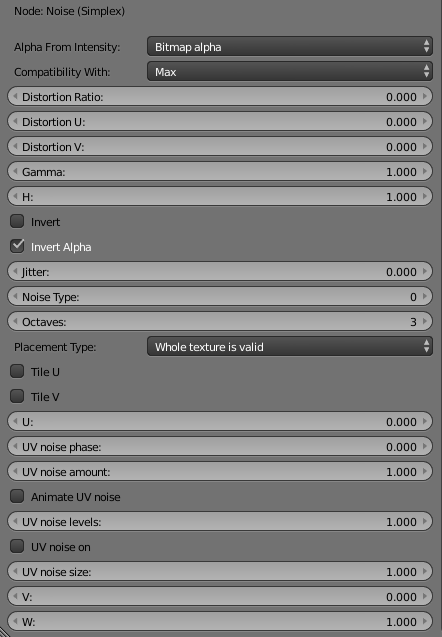
Parameters
Alpha From Intensity – Specifies where to take the alpha from.
Bitmap alpha – This is the default setting. With this option selected, V-Ray renders the material the same on both sides.
Color intensity/luminance – Renders the backside of polygons as invisible for the camera.
Force opaque – Renders the backside of polygons as invisible to all rays, except shadow rays.
Compatibility – Allows you to match the result of the texture in Blender to that in either 3ds Max or Maya. If Alpha From is set to Maya:
3ds Max – The resulting alpha of the texture is the intensity of the texture.
Maya – The resulting alpha of the texture is the color luminescence.
Distortion Ratio –
Distortion U/V –
Gamma –
H – Specifies the height of the texture sector.
Invert – When enabled inverts the colors in final result.
Invert Alpha – Inverts the alpha channel if Invert is also enabled.
Jitter – The amount of random placement variation.
Noise Type –
Octaves – Controls the number of functions to use when calculating Perlin Noise.
Placement Type – Select how to place the texture.
Whole texture is valid
Crop
Place
Tile U/V – Enable to choose between a horizontal or vertical tiling.
U – U coordinate of the texture sector.
UV noise phase – Specifies the UV noise iterations.
UV noise amount – Specifies the UV noise amount.
Animate UV noise – If enabled, the noise is animated. Use the UV noise phase to animate the noise.
UV noise levels – Specifies the UV noise iterations.
UV noise on – Enables the noise.
UV noise size – Specifies the UV noise size.
V/W –
Reference
[*] Ken Perlin, Noise hardware. In Real-Time Shading SIGGRAPH Course Notes (2001), Olano M., (Ed.). (pdf)