This page contains information about the Chaos Scatter geometry and the Chaos Scatter Surface Color texture and their integration in V-Ray.
The Chaos Scatter geometry and the Chaos Scatter Surface Color texture are not available in previous versions of V-Ray.
For more information on working with Chaos Scatter, please visit the following Chaos Corona pages:
Getting Started with Scatter for 3ds Max
Scatter for 3ds Max - Advanced Features
Performance and Troubleshooting
Scatter Geometry Overview
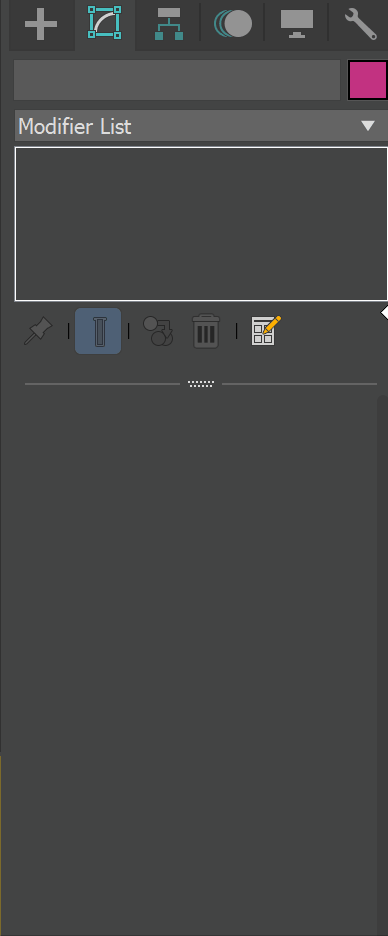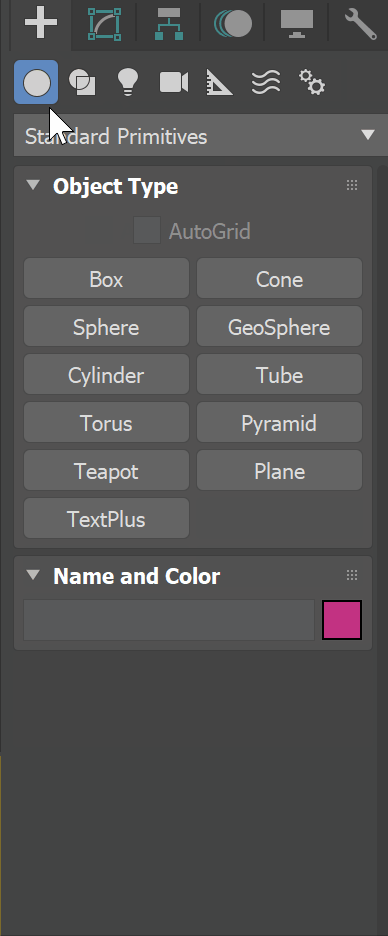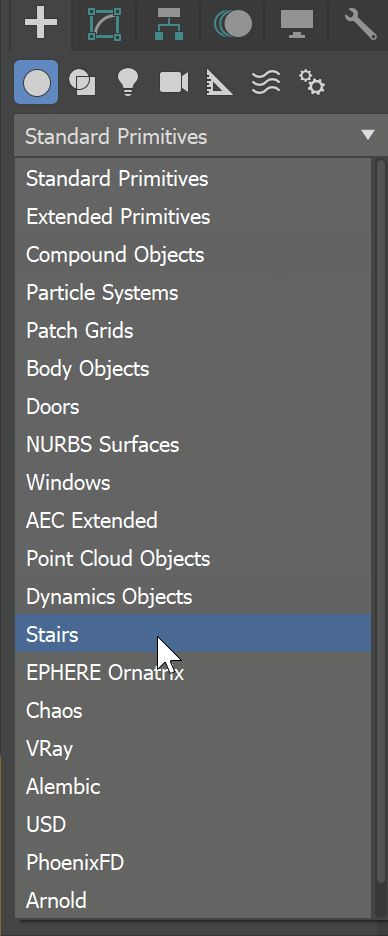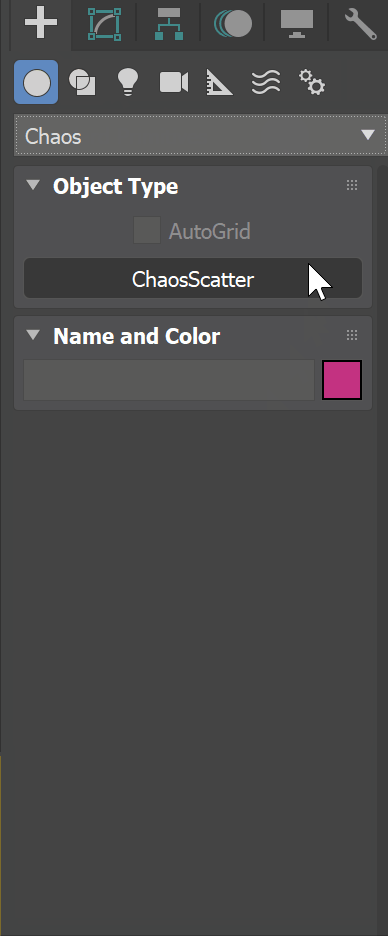
Chaos Scatter is a powerful instancing and distribution tool that allows you to easily populate scenes with selected objects. This is especially useful for outdoor scenes that need to be filled with greenery, rocks, grass etc.
Chaos Scatter is also available with the Corona renderer. For more information, please visit the Chaos Scatter page for Corona.
Workflow
This video tutorial for the Corona renderer showcases common uses for Chaos Scatter's options, such as Normal vs. Z, Slope Limitation, Spline includes and excludes, Camera Clipping and more. Please also see the end of the video for a workflow using Chaos Scatter Surface Color texture.
Loading Chaos Scatter files from arbitrary location
To load Chaos Scatter files from a non-default location, follow the steps below:
- Install V-Ray for the respective 3ds Max version you use.
- Copy the "C:\Program Files\Chaos Group\Scatter" folder to the file server, e.g. \\fileserver\Scatter.
- Copy "C:\Program Files\Autodesk\3ds Max 20NN\Plugins\ChaosScatterMax20NN.dlt" to the file server, e.g. \\fileserver\ScatterPlugin\ChaosScatterMax2023.dlt. Replace the 20NN with your 3ds Max version.
- Then, uninstall V-Ray.
Set the following environment variable (you can use .bat file or system/user environment variables). Pay attention to the version of 3ds Max in both environment variable name and value - they should be the same:
"CHAOSSCATTER_3DSMAX_20NN_LOAD_PATH=\\fileserver\Scatter\3ds Max 20NN"
You can download an example .bat file set for 3ds Max 2023 here. It sets an environment variable for 3ds Max 2023 and then, opens 3dsmax.exe.Launch 3ds Max and from the Customize menu select Configure User and System Paths.
From 3rd Party Plug-Ins click Add and browse the path where ChaosScatterMax20NN.dlt file is copied, e.g. \\fileserver\ScatterPlugin\ChaosScatterMax2023.dlt.
Close 3ds Max and reopen it, Chaos Scatter plugin should be loaded and ready for usage.
Replace the 20NN with your 3ds Max version in all of the shown paths. The examples given are for 3ds Max 2023.
Objects
Distribute on-target objects – Specifies the object(s), on which the instances will be scattered.
Factor – This option is only available when Surface Scattering is set to Random or the scattering mode is set to 3D - In Bounding Box. Determines how many instances are scattered on the currently selected Distribute on-target object.
Instanced model objects – Specifies the objects which will be scattered on the distribute on-target object(s).
Frequency – This option is only available when there are more than one Instanced model objects. Determines the frequency of the currently selected instanced object in relativity to the others.
Override node properties – When enabled the node properties for the scatter node will override those of the individual instanced model objects. (f.e. primary and secondary visibility, V-Ray matte options etc.)
Scattering
Enable – Enables scattering.
1D - On splines – Scattering mode where objects are scattered along splines. Open or closed splines can be used for this.
2D - On surfaces – Scattering mode where objects are scattered on surfaces. It doesn't matter if the surface is horizontal, vertical or if it is part of a complex 3D object. Closed splines can also be used with this mode. In that case, instances are distributed in the area enclosed by the spline.
3D - In bounding box – Scattering mode where objects are scattered inside the object's bounding box. Keep in mind that bounding boxes are cube-shaped, therefore using this mode on a round object scatters instances in a cube around it. This mode is useful when scattering dust particles inside a room, fish in an aquarium, books on a bookshelf and similar.
Max. limit – Limits the maximum number of instances. Note that this option does not determine how many instances are created. Instead it serves as a measure to avoid scattering too many instances and causing a crash.
Random seed – Determines the random distribution used. Changing this value causes random permutations of the scattered objects(s).
Temporal consistency – When enabled, instances are scattered in the selected Rest-pose frame and stick to the surface, even if it gets deformed in other frames. Otherwise, instances get scattered in each frame separately and that might cause anomalies.
Rest-pose frame – Determines the initial frame, where the instances are scattered for all following frames.
Avoid collisions – When enabled, instances that would collide with each other get discarded. This results in no overlaps between instances. Note that enabling this option might lower the number of instances.
Spacing [%] – Controls the size of the bounding boxes used to detect collisions. Smaller values result in denser instances with some collision, higher values result in larger distances between instances. Values above 100% mean that the distance between objects is larger than their bounding boxes.
If the Temporal consistency option is enabled, Avoid collisions does not apply to frames outside of the initial Rest-pose frame.
Edit Instances – Switches to ' Instances' sub-object mode. This allows individual instances to be manipulated. Only the instances visible in the viewport can be edited. This option is only useful for small numbers of instances, otherwise it might cause a crash. If you select 100 or more instances, Chaos Scatter will display a warning. To switch out of this option, click on Edit Instances one more time. The edited instances are ignored by the Avoid collisions option, the Include/Exclude splines option, Slope limitation and by Camera clipping.
Keep in mind that if you edit the original model of the scattered instances, after you've edited them, they will be reset back to their original state. To avoid this, edit your instances after finalizing the state of the original model and the Scatter.
Convert to Max geometry – When enabled, this option converts the Chaos Scatter instances into 3ds Max instances. This option is only useful for small numbers of instances, otherwise it might cause a crash.
Scatter Lister – Opens the Chaos Scatter Lister. It can be used to toggle individual scatters on and off and to control their properties such as displayed amount, scattering count and limit, names, and more.
Camera clipping
Enable – When enabled, instances are limited to a camera view. The rest are clipped away. This option may improve scene parsing performance and lower memory requirements. It is disabled by default.
The Camera clipping tool is an optimization tool. It is not intended for limiting instances to a certain area and should not be used for that purpose. It is recommended to use other tools for limiting instance spread, such as the Areas option.
Active render camera – This mode uses the camera from the current viewport to clip instances. If the parameters are left at default, the clipping will not be visible in the viewport, allowing editing while the instances are optimized at the same time. With a reasonable Extend view value, this mode is recommended for optimizing your scene. It works automatically, so it automatically saves scene parsing time and RAM usage.
Specific scene camera – This field below allows you to select a camera from the scene to use for clipping. In this case the clipping is always visible in the viewport.
Extend view – Specifies an extension to the camera view in all directions. All instances inside the Extend view are not clipped.
The Camera Clipping tool could cause some missing shadows and/or reflections. The Extend view option can be used to amend that by allowing some extra space for those details to be included.
Near and Far overrides – Specifies the near - and far threshold distances from the camera. The near threshold value determines the minimum distance from the camera, before which instances are clipped. The far threshold distance determines the maximum distance away from the camera, after which instances are clipped. This option gives extra control over the clipping. It is disabled by default.
Spline Scattering
This submenu is only available when the scattering mode is set to 1D- On splines.
Spacing – Determines the spacing between instances in world units.
Jitter [%] – Randomly jitters instances along the spline. Each instance has Spacing applied on both its sides, except the instances at the end of the spline. The Jitter value is divided between those two Spacings. In order to allow instances to jitter in all their Spacing distance, the Jitter needs to be set to 200%.
Offset [%] – Determines what percentage of the Spacing the instances are offset in one direction of the spline. When set to 100%, all instances replace the one after them, as the offset is equal to the whole value of the Spacing.
Follow spline [%] – Determines how scattered instances are oriented along the spline. Assigning a value of 100%, makes instances follow the spline and are oriented along the local tangent direction.
Surface Scattering
This submenu is only available when the scattering mode is set to 2D - On surfaces.
Random distribution – This mode scatters instances randomly on all mesh and closed spline distribution objects. It is enabled by default.
Count – Determines the exact number of instances to scatter. If the Per square option is enabled, the scattering is defined by the density.
Per square – When enabled, the Count amount is multiplied by the specified edge length (value next to Per square).
Map – Allows a black and white texture map to be assigned. The map determines how the instances are scattered on the surface.
UV map – This mode uses UVW mapping to scatter instances in regular patterns.
Pattern – Determines a pattern to use for scattering.
Grid – Rectangular grid.
Running grid – Rectangular grid with every other row offset by half of the grid spacing.
Hex grid – Arranges instances into hexagons.
UV channel – Determines the UV channel.
Override by planar mapping – When enabled, a simple planar UVW mapping is created and used instead of the pre-existing UVW channels.
Lock V – When enabled the values of the V coordinate for Spacing, Jitter and Offset are locked to the U coordinate's values.
Spacing [%] – Scales the pattern in UV space. When Spacing is set to 100%, the pattern occupies the whole space. When Spacing is set to 50%, the pattern is repeated twice.
Jitter [%] – Determines what percentage of the instances are randomly placed. When Jitter is set to 0, all instances are placed according to the UVW mapping. When Jitter is set to 100, all instances are randomly placed.
Offset [%] – Offsets the pattern by the given value (in percentages). Keep in mind that 0% and 100% Offset gives the same result, as 100% moves the pattern by one whole repetition.
Slope Limitation – This option limits scattering only to 'slopes' at certain angles. It can be used to create realistic spread of trees on curved surfaces, for instance. The lower the Angle range is set, the smaller the angle at which scattering stops.
Angle – Defines a range of angles to which the scattering is limited. Instances outside of this range get filtered out. The angles are measured either between the Local up vector and the surface normal, or the World up vector and the surface normal. You can select which up normal to use in the option below.
Local – When enabled, the Slope Limitation is measured according to the up vector of each individual Distribute-on target object.
World – When enabled, the Slope Limitation is measured according to the world Z-axis up vector for all Distribute-on target objects in the scene.
Bounding Box Scattering
This submenu is only available when the scattering mode is set to 3D - In bounding box.
Count – Determines the exact number of instances to scatter. If the Per cube option is enabled, the scattering is defined by the density (Per cube).
Per cube – When enabled, the Count amount is multiplied by the specified edge length (value next to Per cube).
Transformations
Translation
Moves the instances From the given distance To the given distance on the corresponding axis. A map can be attached. If the map is enabled, it overwrites the translation values. RGB maps can be used to control translations in specific axes (Red = X; Green = Y; Blue = Z). Grayscale maps control all axes proportionally.
Mode – Determines how the map is interpreted to control the translation.
Map fixed – Black areas of the map represent the From values. White areas of the map represent the To values. No randomization occurs.
Random amount – Black areas of the map do not have any randomization applied. In the white areas of the map full randomization occurs. The From and To values represent the lowest and highest translations allowed for the randomization.
Stepping distance – Determines a distinct distance between all instances in the enabled axes. If the values is left at zero, instances are translated continuously.
Rotation[°]
Rotates the instances From the given degrees up To the given degrees continuously. A map can be applied. If it is enabled for a given axis, its rotation values are overwritten by the map. RGB maps can be used to control the rotation of each axes individually ( Red = X; Green = Y; Blue = Z). Grayscale maps control the rotation of all axes proportionally.
Mode – Determined how the map is interpreted to control the rotation.
Map fixed – Black areas of the map represent the From values. White areas of the map represent the To values. All values in between are on the grayscale spectrum. No randomization occurs.
Random amount – Black areas of the map have no randomization applied. In white areas of the map full randomization occurs. The From and To values specify the lowest and highest rotation allowed for the randomization.
Stepping angle – Determines a fixed degree by which all instances rotate for the enabled axes.
Normal vs. Z – When a value different than 0 is entered, the instances are aligned according to the world Z axis. This is useful when the Distribute-on target object is curved and the scattered objects need to remain vertical, not follow the curve of the surface. Positive values mean that the instances are aligned to the +Z axis (vertical up) and negative values mean that the instances are aligned to the -Z axis (vertical down).
Preserve model rotation – When enabled, instances preserve the original rotation of the Instanced model object. Otherwise. the original rotation is ignored.
Scale [%]
Scales the instances From the given value To the given value continuously. When Uniform scale is enabled, the X axis values are applied on the whole Distribute-on target object. A map can be applied. If it is enabled for an axis, the values of that axis are overwritten. RGB maps can be used to scale axes individually ( Red = X; Green = Y; Blue = Z). Grayscale maps control the scale of all axes proportionally.
Mode – Determines how the map is interpreted to control the scale.
Map fixed – Black areas of the map represent the From values. white areas of the map represent the To values. All values in between are on the grayscale spectrum. No randomization is applied.
Random amount – Black areas of the map have no randomization applied. In white areas of the map full randomization occurs. The From and To values represent the lowest and highest scale allowed for the randomization.
Legacy – The From values determine the areas where full randomization occurs. The To values determine areas where no randomization is applied. Black areas of the map have zero scale. White areas of the map have maximum scale.
Stepping percentage – Determines a percentage of scaling to be applied to all instances. Otherwise, scaling is continuous.
Uniform scale – When enabled, all instances in all axes are scaled according to the values of the X axis.
Preserve model scale – When enabled, instances preserve the original scale of the Instanced model object.
Areas
Spline includes – This option scatters the models only inside the splines included in this list. The splines cannot be the same as the Distribute-on target objects.
Spline excludes – This option scatters the models everywhere on the Distribute-on target objects, except in the areas where the splines from the list are located. The splines cannot be the same as the Distribute-on target objects. This option is useful, for instance, for removing instances of grass/trees from areas where a house needs to be located.
Near/Far – This option is only active when a spline from either list is selected. Determines the falloff distance from the selected spline to the selected axis plane (Projection). If the selected spline is from the Spline includes list, instances within the falloff distance are included. If the selected spline is from the Spline excludes list, instances within the falloff distance are excluded. For more information, see the Spline include Animation Example.
Scale – Scale factor further affecting the instances between the near and far falloff.
Density – Density factor further affecting the instances between the near and far falloff.
Spline include Animation Example
Chaos Scatter parameters can be animated. In this example, the Spline includes list is animated. Using the Near and Far parameters, you can create effects like growing a forest.
Viewport Display
Instances
Previz type – Determines the way the instances are displayed in the viewport. This is not reflected when rendering.
None – Does not display anything.
Dot – Displays each instance as a dot.
Box – Displays each instance as a solid box
Wire box – Displays each instance as a wireframe of a box.
Full – Displays the full geometry of the model.
Point cloud – Displays the instance as a series of dots in the shape of the original model.
Max instances – Determines the maximum number of instances displayed in the viewport. When this limit is exceeded, random instances are hidden. If increasing this number would display more instances, the option is colored.
Max polygons – This option is only available when the Previz type is set to Full. Determines the maximum number of polygons in the viewport. When this limited is exceeded, random polygons are hidden. The option is colored, when the value does not correspond to the maximum number of polygons available for display.
Points [%] – This option is only available when the Previz type is set to Point cloud. Determines the percentage of points to be displayed in the viewport.
Original wire colors – When enabled, instances are colored using the original model's wire colors. Otherwise, the instances use Chaos Scatter's wire colors. An object's wire colors can be found in the Modify menu next to its name.
Icon Size – Determines the size of the Chaos Scatter object's gizmo in the viewport.
Update automatically – When disabled, scattering is not recomputed when either the Distribute-on target objects or the Instanced objects are changed. This option does not affect changes in the Chaos Scatter parameters. Changes to the parameters always trigger recomputation.
Update now – Forces recomputation of the scattering.
Info
This section displays information about the selected Chaos Scatter geometry.
Instances – Displays the total number of instances creates by the selected Chaos Scatter.
Polygons – Displays the total number of polygons created by the selected Chaos Scatter.
About Chaos Scatter – Displays information about the current Chaos Scatter.
Scatter Surface Color Texture Overview
The Chaos Scatter Surface Color texture is used with Chaos Scatter, to color the created instances according to the surface diffuse of the underlying Distribute-on target object. For instance, if the underlying object has a checkered map applied to its diffuse slot, applying a Scatter Surface Color texture will make the instances checker-colored as well. This can be useful, for instance, for creating patterned furry carpets. The Scatter Surface Color comes with V-Ray 6.
Chaos Scatter Surface Color texture is also available with the Corona renderer. For more information, please visit the Chaos Scatter Advanced Features for Corona page.
Parameters
Source – Determines whether Chaos Scatter Surface Color uses a custom map, which you can pick from the button below. By default, the surface diffuse of the Distribute-on target object is used.
Hue random [%] – Controls hue randomization of the resulting hue. Specifies percentage, where 0% disables randomization and 100% applies maximum randomization.
Gamma random [%] – Controls the randomization of the midtones (gamma) of the result. Specifies percentage, where 0% disables randomization and 100% applies maximal reasonable randomization.
Chaos Scatter Surface Color texture example
This example shows how instances are colored according to the underlying object's texture. Chaos Scatter Surface Color texture is applied to the original model of the instances.