Bump
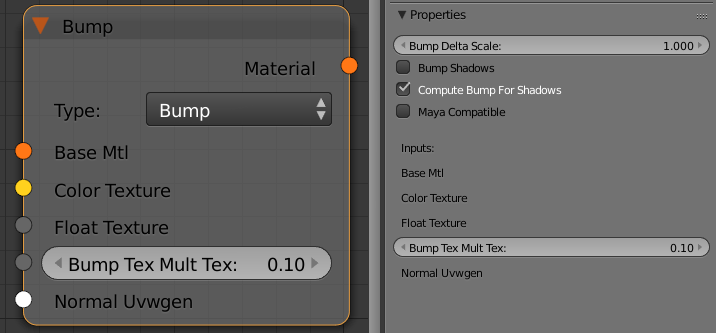
The Bump node allows you to add bump map or normal map effects when using any material.
Bump Delta Scale - scale for sampling the bitmap when using bump mapping. The exact value is calculated automatically by V-Ray, but can be scaled here.
Maya Compatible - when enabled V-Ray will render the bump mapping in such a way that it matches the result that can be achieved in Maya.
Bump Shadows - when this option is checked V-Ray will consider the bump maps when rendering shadows produced by objects with the bump material applied to them.
Type - allows the user to specify whether a bump map or a normal map effect will be added to the base material.
- Bump - normal bump map
- Normal (Tangent) - normal map in tangent space
- Normal (Object) - normal map in object space
- Normal (Camera) - normal map in camera space
- Normal (World) - normal map in world space
- From Bump -
- Explicit Normal -
Base Mtl - allows you to select the base material to which the bump/normal effect will be added.
Color Texture - you can use this slot to connect any 8bit texture
Float Texture - you can use this slot to connect a texture in a floating point format
Bump Tex Mult Tex -a multiplier for the strength of the bump/normal effect
Normal Uvwgen - connect a mapping node here.
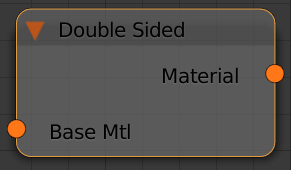
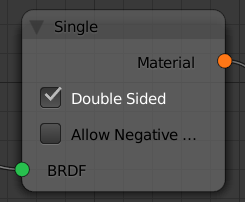
Double Sided
This node will flip the normals for back-facing surfaces with this material assigned.
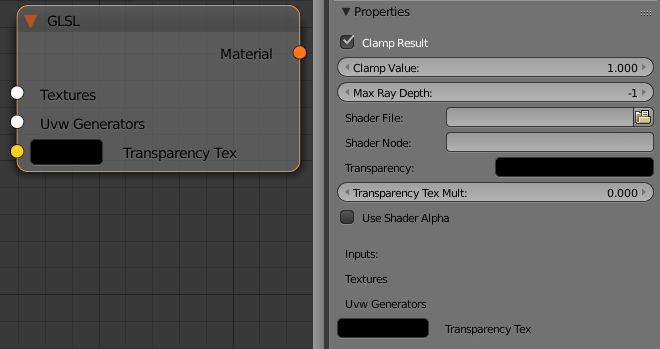
GLSL
This node can be used to load GLSL shaders (.frag, .glsl files), V-Ray precompiled fragment shaders (.pfrag files) and render them directly with V-Ray.
See the V-Ray GLSL page for more detailed description of the language and examples.
This node is the first stage of the V-Ray implementation of GLSL support. In this version, the shaders are compiled to byte code for a software virtual machine, which is then interpreted. Due to this run-time interpretation, GLSL shaders can be somewhat slower to render than V-Ray shaders written in C++. In future builds of V-Ray, shaders will be directly compiled to machine code for faster rendering.
Clamp Result - determines whether to force the result in the [0, Clamp Value] range or not.
Clamp Value - specifies the upper clamp limit if Clamp Result is enabled.
Max Ray Depth - specifies the maximum reflection/refraction depth for the shader.
Shader File - specifies the .glsl, .frag, or .pfrag file which contains the shader code.
Shader Node - specifies a custom name for the shader node
Transparency - override the alpha if Use Shader Alpha off. You can use either a single color or a texture for that parameter.
Transparency Tex Mult - a multiplier for the Transparency parameter when a texture is used
Use Shader Alpha - use the alpha calculated in the shader.
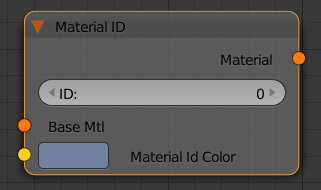
Material ID
This node allows you to assign an ID number to any material in your scene. This ID can be later to extract a mask for all objects with that material using the MultiMatte render element.
Base Mtl - a slot for the material that the ID will be assigned to
ID - a unique identification number for that material
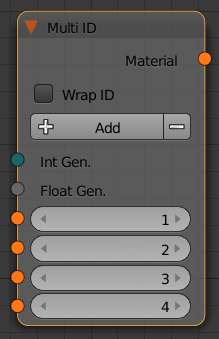
Multi ID
This node allows you to assign different materials on a single mesh based on face IDs.
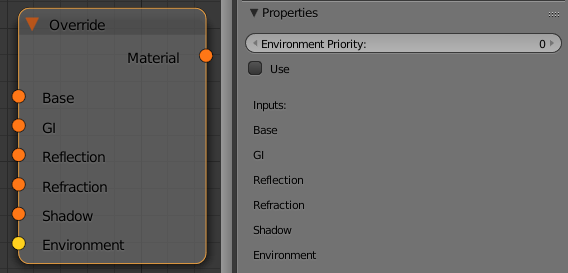
Override
This node allows a surface to look different depending on whether it is seen through reflections, refractions, or GI. With this material you can get a fine control over the color bleeding, reflections, refractions, and shadows of the objects.
Environment Priority - this specifies how to determine the environment to use if a reflected or refracted ray goes through several materials each of which has an environment override.
Base - this is the material V-Ray will use while rendering the object.
GI - this is the material V-Ray will use while calculating the GI solution.
Reflection - this is the material V-Ray will use to render the object with, when the object is seen in reflections.
Refraction - this is the material V-Ray will use to render the object with, when the object is seen in refractions
Shadow - this is the material that will be used to render shadows cast from the object.
Environment - this is an environment override for the Base Material
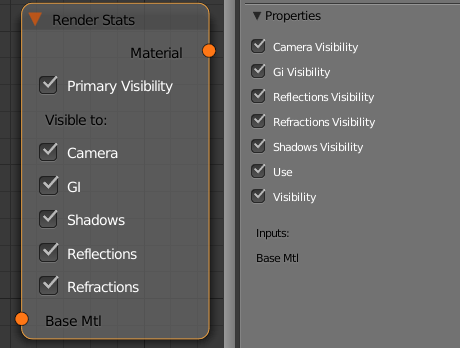
Render Stats
This node allows you to make the object invisible to different rays during rendering.
Primary Visibility (Visibility) - controls the total visibility of the object
Camera - controls the visibility of the object for the camera rays
GI - controls the visibility of the object for GI rays
Shadows - controls whether or not the object casts shadows
Reflections - controls the visibility of the object in reflections
Refractions - controls the visibility if the object in refractions
Use - enables the Render Stats node
Round Edges
This node uses bump mapping to smooth out the edges of the geometry during render time
Radius - specify a radius (in world units) for the round edges effect. Since the actual geometry is not being changed and only the normals of the faces are affected large values here may produce undesirable effects.
Round Edges
This node uses bump mapping to smooth out the edges of the geometry during render time
Radius - specify a radius (in world units) for the round edges effect. Since the actual geometry is not being changed and only the normals of the faces are affected large values here may produce undesirable effects.