This page provides information about the Angle Blend material in V-Ray for Blender.
Overview
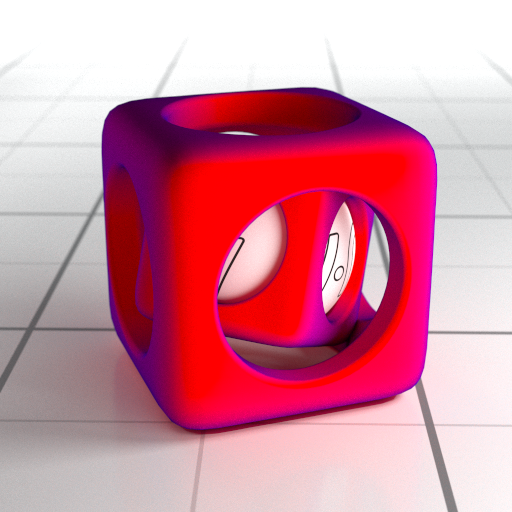
The Angle Blend material allows you to make a blend between two materials. The angle of blend depend of the view direction and the surface normal. V-Ray can use several blend functions to determine the blended result. It can be used to create complex materials like car paints, velvet, pearl, etc.
UI Path
||Node Editor|| > Add > Material > Angle Blend
Node
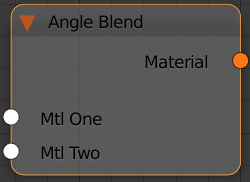
Material – An output slot for the Angle Blend material.
Mtl One – Sets the material to be used on the area perpendicular to the view direction.
Mtl Two – Sets the Material to be used on the area parallel to the view direction.
Parameters
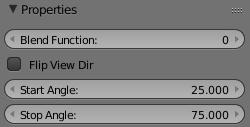
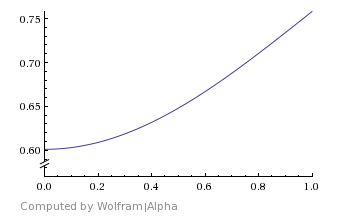
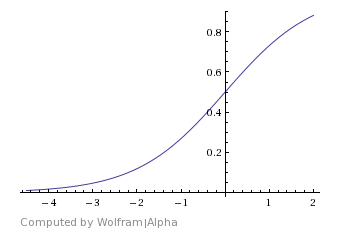
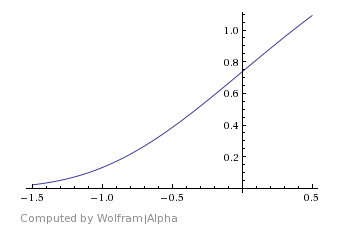
Blend Function – Specifies the specific method for V-Ray to calculate the blended result. For more information, please see Blend Function Diagrams below.
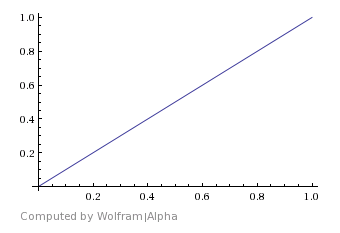
Linear – A straight linear progression from material 1 to material 2.
Normal Distribution – Starts approximately evenly blended between material 1 and 2 and then gradually transitions to material 2.
Sigmoid – A slow curve that eases out of material 1 with the Start Angle before smoothing out in the middle, and then easing into material 2 at the end with the Stop Angle.
Gompertz – A curve similar to Sigmoid, but slightly faster at reaching a point where the materials are blended.
Cube Root – A smooth curve blending from material 1 to material 2 that rapidly jumps around the middle of Start and Stop angles and then returns to a smooth curve.
Cubic – Rapid progression from material 1 to material 2 that slows down briefly around the middle of Start and Stop angles before resuming fast progression toward material 2.
Cubic Polynominal – A smoother cubic shape with a longer hold in the center of the blend than Cubic
Flip view direction – When enabled, reverses the direction of the blend.
Start Angle – Specifies the angle in which the blend will begin.
Stop Angle – Specifies the angle in which the blend will end.
Blend Function Diagrams
Linear
Normal Distribution
Sigmoid
Gompertz