Page History
...
General
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| UI Expand | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
$(scene_path) – $(dir)\$(scene)_Phoenix_frames\$(nodename)_####.aur #### is the frame number formatted with at least as many digits as the hash signs. If the frame digits are less than the hashes, the number is padded with zeroes to the left. For example:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UI Text Box | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Since version 3.00.02, Phoenix can export VDB grid data. Check the How to export Phoenix FD simulation to OpenVDB format video. Particle data can also be exported using the .aur or the .vdb format. Phoenix can convert particles from already simulated Phoenix .aur caches into the .prt format as a post-process using the Chaos Phoenix Export PRT Particles dialog or to .vdb format using the Cache Converter tool. |
...
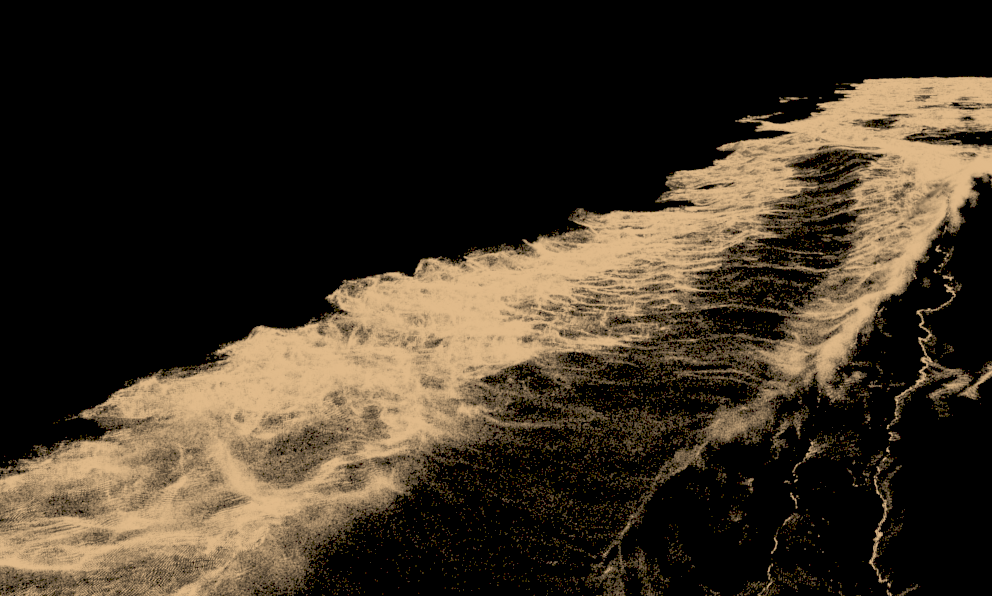
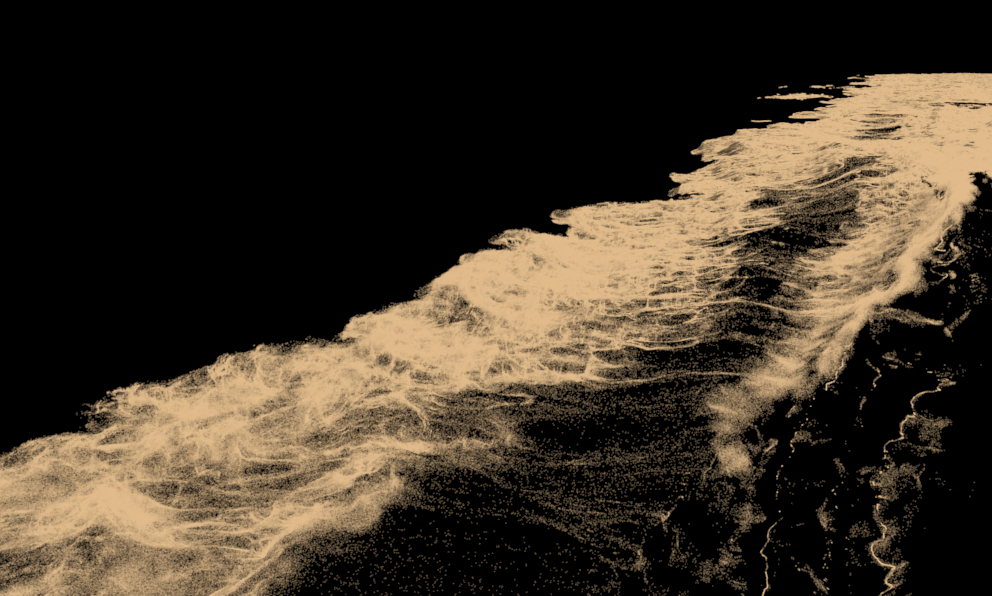
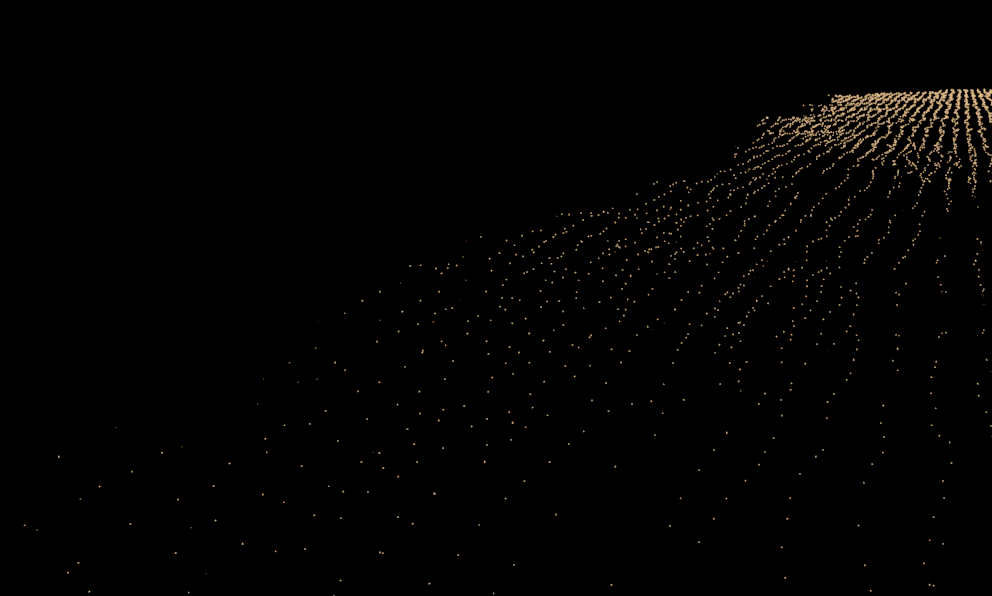
Storage Quality | storage_quality – The output grid and particle channels in AUR files are compressed by default in order to increase the performance (faster cache loading) and to avoid excessive memory consumption. This parameter can range from 8 to 20 - 8 is the smallest size, while 20 is the best quality and is uncompressed. If this value is set too low, different artifacts may start appearing depending on the type of scene. For grid channels, artifacts shaped like horizontal slices may appear in preview and rendering. For particle systems such as Liquid or Foam, the artifacts would look like ordered lines of particles , as in the following comparison (click to zoom in):(see the Particle compression artifacts example below).
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| UI Text Box | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
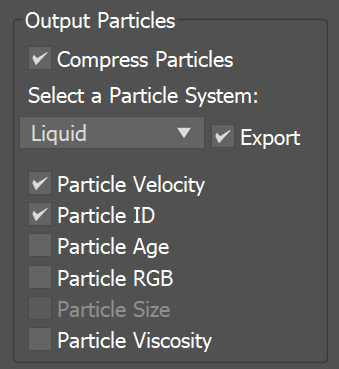
The particle export parameters share a user interface to keep the user interface compact. Each particle system can be selected individually from the drop-down list, and the output settings can be selected for that particle system. When a particle system is selected again, the same settings are retained. |
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Example: Particle compression artifacts
|
...
| UI Text Box | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
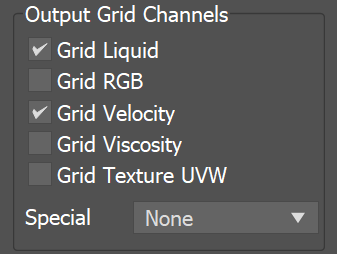
This section determines which channels are exported to cache files in the form of a voxel grid. Currently, only the liquid particles can be automatically converted to a grid during export, while all the other systems (e.g. Foam, Splash, etc.) are exported only as particles. |
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...