Page History
This page provides an overview of the GI tab of the VRayRenderer node.
Overview
...
Global Illumination (or GI) is the illumination in a scene that comes from reflected (or bounced) light as opposed to coming directly from a light source. This enables more naturalistic and accurate lighting solutions.
The indirect illumination controls in V-Ray are divided into two types: primary diffuse bounces and secondary diffuse bounces.
| Fancy Bullets | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
More Information on how V-Ray calculates indirect Illumination can be found on the Indirect Illumination Reference page.
...
UI Path: ||Select VRayRenderer|| > Properties Panel > GI tab
Parameters
...
...
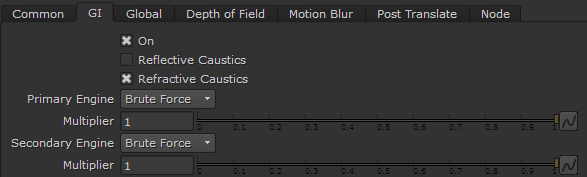
On – Enables/disables global illumination.
...
Brute Force – Selects the brute force method (direct computation) for primary diffuse bounces. For more information on the Brute Force engine, please see the Brute Force Information page.
Light Cache – Selects the light cache method as the primary GI engine. For more information on the Light Cache engine, please see the Light Cache Information page.
Multiplier – Determines the degree to which primary diffuse bounces contribute to the final image's illumination. Note that the default value of 1.0 produces a physically accurate image. Other values are possible, but not physically accurate.
...
Brute Force – Selects the brute force method (direct computation) for secondary diffuse bounces. For more information on the Brute Force engine, please see the Brute Force Information page.
Light Cache – Selects the light cache method as the secondary GI engine. For more information on the Light Cache engine, please see the Light Cache Information page.
Multiplier – Determines the effect of secondary diffuse bounces on the scene illumination. Values close to 1.0 might wash out the scene, while values around 0.0 might produce a dark image. Note that the default value of 1.0 produces physically accurate results. While other values are possible, they are not physically accurate.
Brute Force
...
The parameters in this rollout will only activate when using Brute Force as a Secondary Engine, due to the Primary bounce only accounting for the first bounce. For more information on how the Brute Force engine works, see the Brute Force Information page.
...
Depth – Controls the number of light bounces that will be computed for secondary bounces.
Light Cache
...
The following parameters are visible from the Light cache rollout when it is selected as a Primary engine or Secondary engine in the Global Illumination Tab of the VRayRenderer node. For more information on how the Light Cache engine works, see the Light Cache Information page.
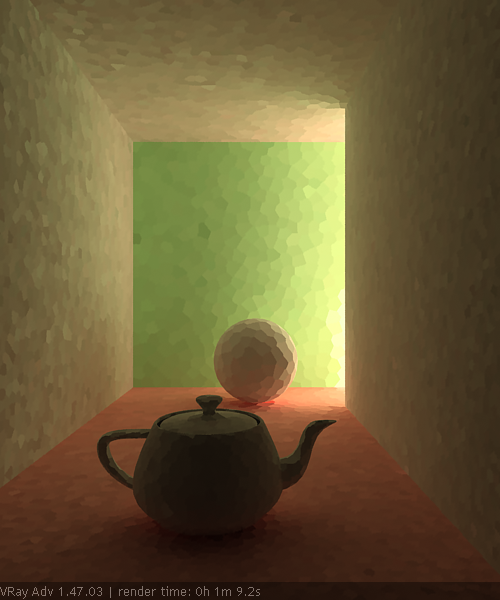
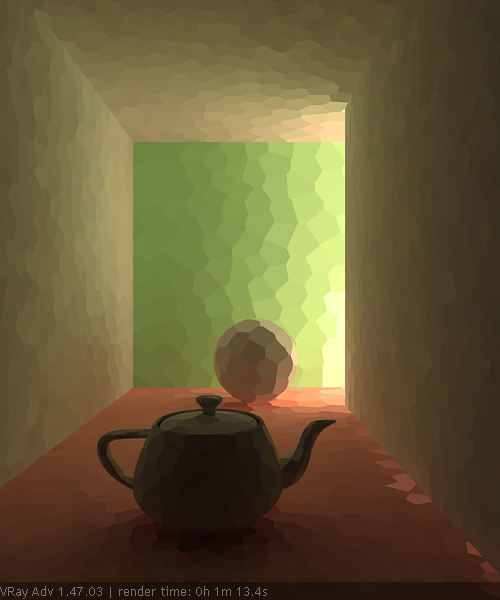
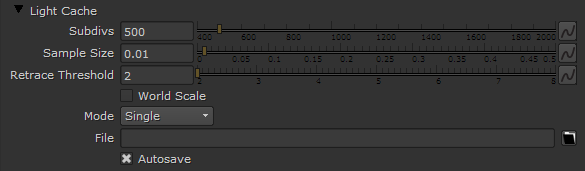
Subdivs – Determines how many paths are traced from the camera. The actual number of paths is the square of this value. The default value of 1000 subdivs mean that 1,000,000 paths will be traced from the camera. For more information, see the Subdivs Parameter example below.
...
| Note |
|---|
Note: Using Fly-through mode will work only when the scene is exported through the VRayTranslator node and rendered in V-Ray Standalone. |
...
File – Specifies the location where the light cache will be saved for later reuse. When the Mode is set to From file the light cache will be loaded from this location.
Autosave – When enabled, the Light cache file will be automatically saved to the location set in the File parameter.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
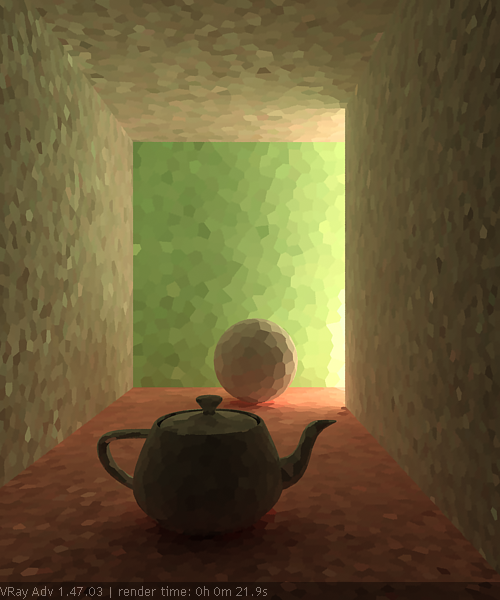
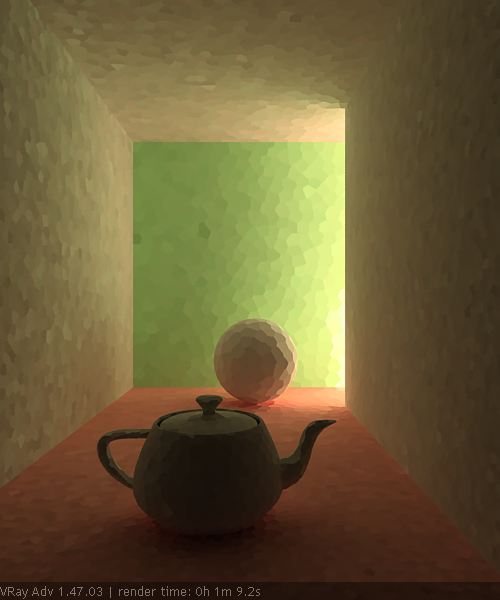
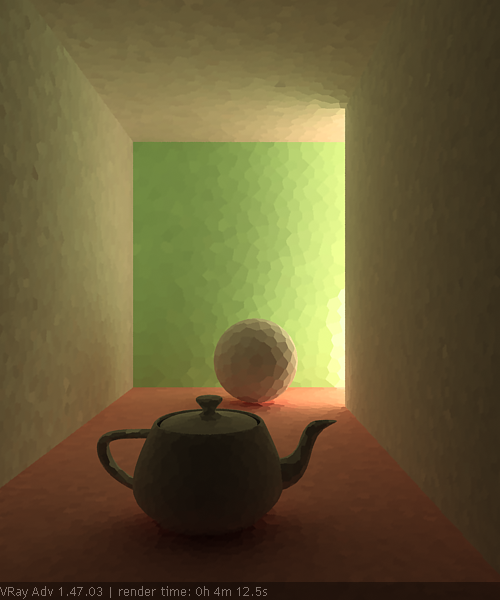
Example: Subdivs Parameter
...
The Subdivs parameter controls the number of rays that are shot into the scene and the noise quality of the light cache samples.
...
As we add more samples, the noise is reduced, but the render times increase. When the Subdivs parameter is doubled, the light cache takes approximately four times longer to calculate.
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
...
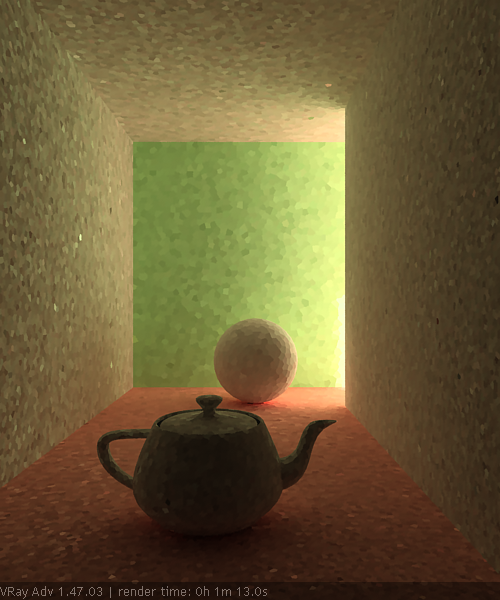
Example: Sample Size
...
The Sample size parameter controls the size of the individual light cache samples. Smaller values produce a more detailed lighting solution, but are noisier and take more RAM. Larger values produce less detail, but take less RAM and may be faster to calculate.
...
Note the light leak from the wall on the right in the last image. This happens because samples from the other side of the wall are quite large and end up being used on the side facing the camera. Also note the difference in the noise level between the samples.
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
...