Page History
...
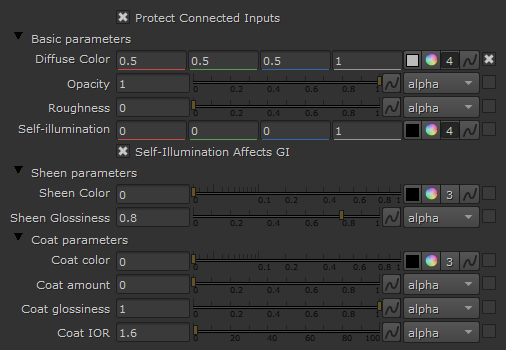
Diffuse
Roughness
Opacity
Self-Illumination
Reflection Color
Reflect Glossiness
Anisotropy
Refraction Color
Refraction Glossiness
Translucency Color
Main Parameters Tab
...
Diffuse Color – The diffuse color of the material. Note: the actual diffuse color of the surface also depends on the reflection and refraction colors.
...
Self-Illumination Affects GI – When enabled, the self-illumination affects global illumination rays and allows the surface to cast light on nearby objects. Note: It may be more efficient to use area lights for this effect.
The Sheen layer can be used for creation of cloth material, such as satin.
Sheen Color – Specifies the color.
Sheen Glossiness – Controls the sharpness of reflections. A value of 1.0 means all of the light reaches the diffuse color, and when the value is smaller, the cloth material looks glossier. See the Sheen Glossiness parameter below for more information.
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Example: Sheen Glossiness
This example shows how changing the glossiness parameter of the sheen layer affects the material. A smaller value makes the sheen layer reflect most of the light. Increasing the value allows more light to reach the diffuse component.
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Coat Color – Determines the coat layer's color. A texture map can be used here.
Coat amount – Specifies the blending weight of the coat layer. A value of 0 does not add a coat layer, while higher values blend the coat gradually. See the Coat Amount example below for more information.
Coat glossiness – Controls the sharpness of reflection. A value of 1.0 means perfect glass-like reflection; lower values produce blurry or glossy reflections. See the Coat Glossiness example below for more information.
IOR – Specifies the Index of Refraction for the coat layer.
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
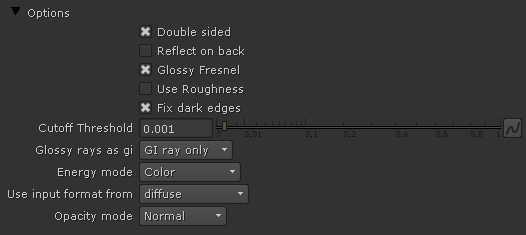
Options Rollout
Double sided – When enabled, V-Ray will flip the normals for back-facing surfaces with this material assigned. Otherwise, the lighting on the "outer" side of the material will
Options Rollout
Double sided – When enabled, V-Ray will flip the normals for back-facing surfaces with this material assigned. Otherwise, the lighting on the "outer" side of the material will be computed always. You can use this to achieve a fake translucent effect for thin objects like paper.
Reflect on back – When disabled, V-Ray will calculate reflections for the front side of objects only. Checking it will make V-Ray calculate the reflections for the back sides of objects too.
Glossy Fresnel – When enabled, uses glossy Fresnel to interpolate glossy reflections and refractions. It takes the Fresnel equation into account for each "microfacet" of the glossy reflections, rather than just the angle between the viewing ray and the surface normal. The most apparent effect is less brightening of the grazing edges as the glossiness is decreased. With the regular Fresnel, objects with low glossiness may appear to be unnaturally bright and "glowing" at the edges. The glossy Fresnel calculations make this effect more natural.
Use Roughness – When enabled, highlights/reflections will be determined by the material's Roughness, otherwise highlights/reflections will be determined by the material glossiness.
Fix dark edges – Enabling will fix dark edges that sometimes appear on objects with glossy materials.
Cutoff Threshold – This is a threshold below which reflections/refractions will not be traced. V-Ray tries to estimate the contribution of reflections/refractions to the image, and if it is below this threshold, these effects are not computed. Do not set this to 0.0 as it may cause excessively long render times in some cases.
Glossy rays as GI – Specifies on what occasions glossy rays will be treated as GI rays:
Never – Glossy rays are never treated as GI rays.
GI rays only – Glossy rays will be treated as GI rays only when GI is being evaluated. This can speed up rendering of scenes with glossy reflections and is the default.
Always – Glossy rays are always treated as GI rays. A side effect is that the Secondary GI engine will be used for glossy rays. For example, if the primary engine is irradiance map, and the secondary is light cache, the glossy rays will use the light cache (which is a lot faster).
Energy mode – Determines how the diffuse, reflection, and refraction color affect each other. V-Ray tries to keep the total amount of light reflected off a surface to be less than or equal to the light falling on the surface (as this happens in the real life). For this purpose, the following rule is applied: the reflection level dims the diffuse and refraction levels (a pure white reflection will remove any diffuse and refraction effects), and the refraction level dims the diffuse level (a pure white refraction color will remove any diffuse effects). This parameter determines whether the dimming happens separately for the RGB components or is based on the intensity:
Color – Causes dimming to be performed separately on the RGB components. For example, a pure white diffuse color and pure red reflection color will give a surface with cyan diffuse color (because the red component is already taken by the reflection).
Monochrome – Causes dimming to be performed based on the intensity of the diffuse/reflection/refraction levels.
Use input format from – Sets the material aspect ratio based on the input format of a connected texture file. This only affects 2D Card nodes that have image aspect enabled.
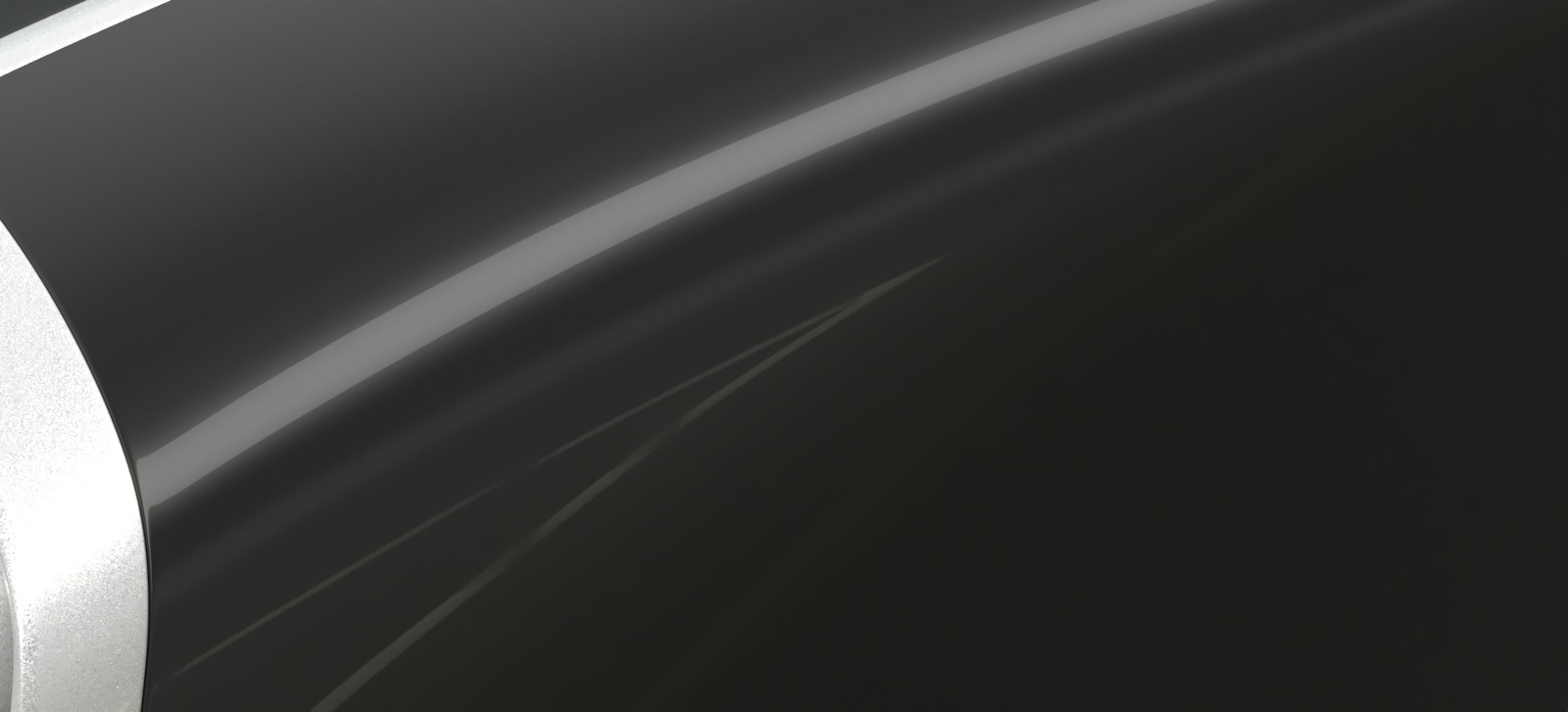
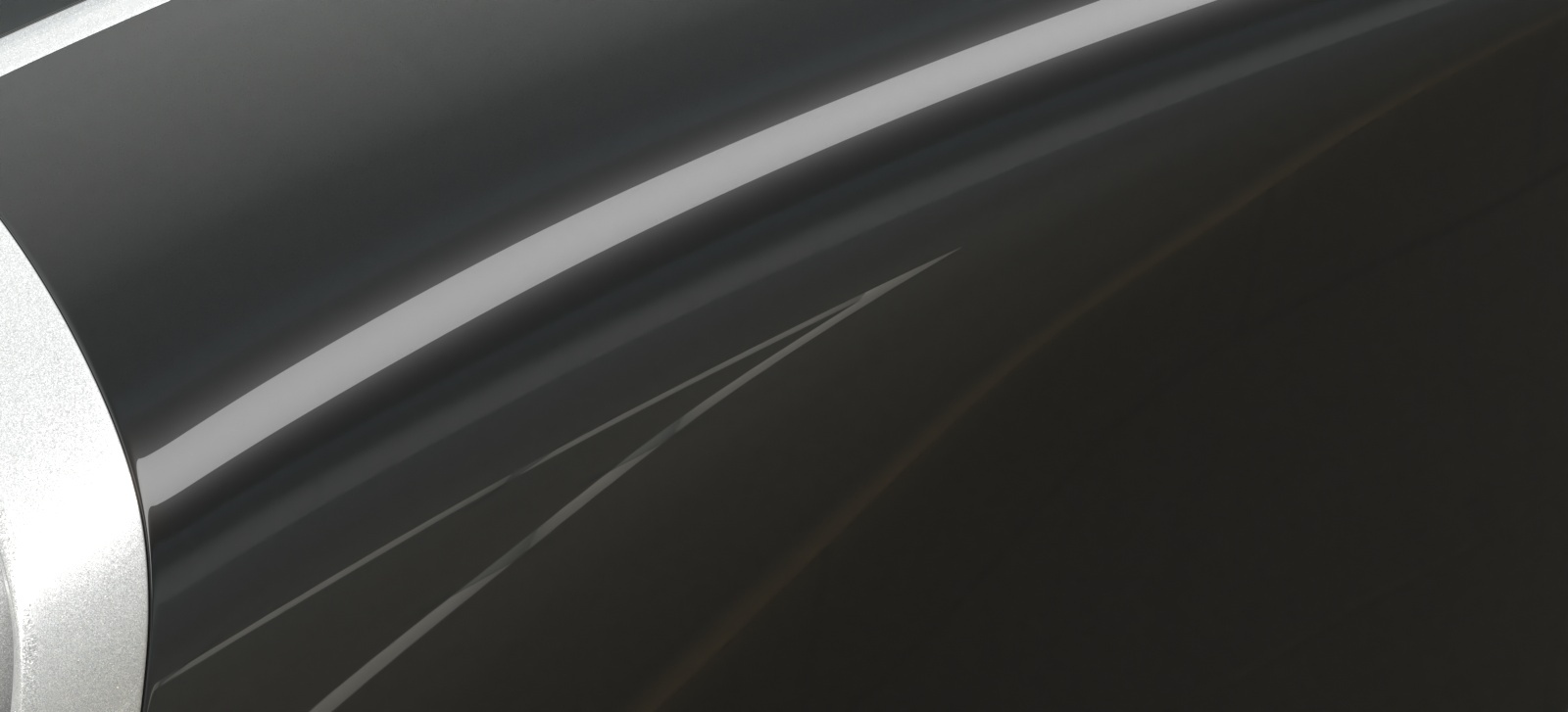
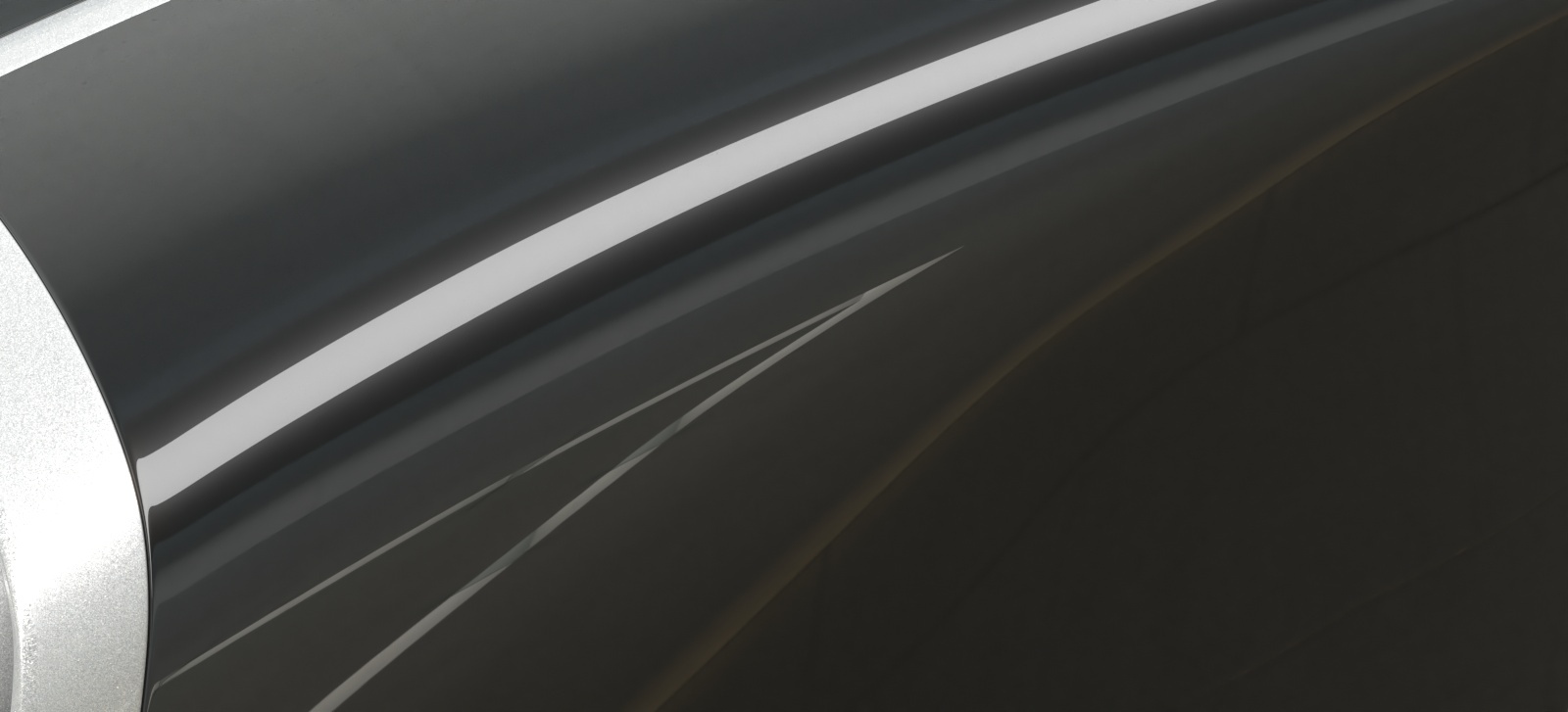
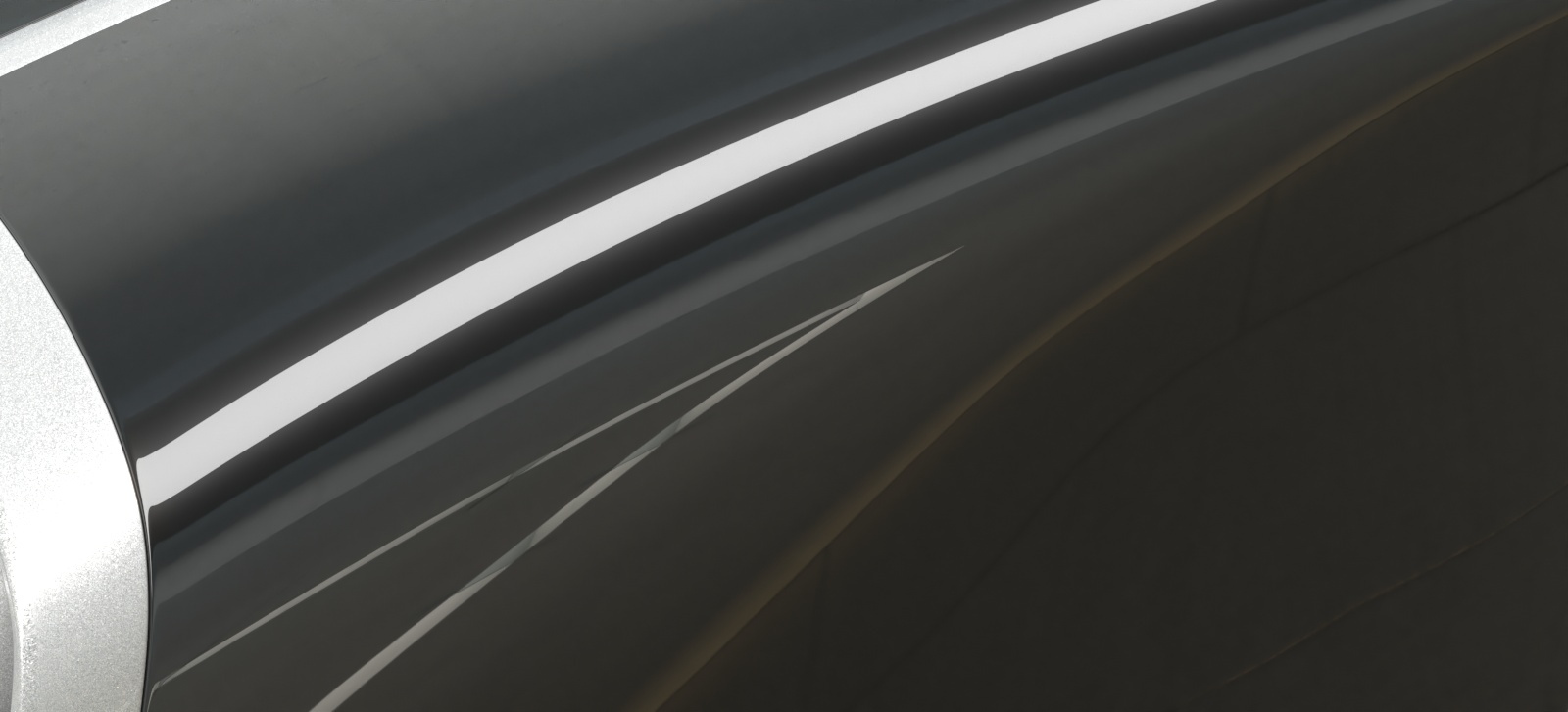
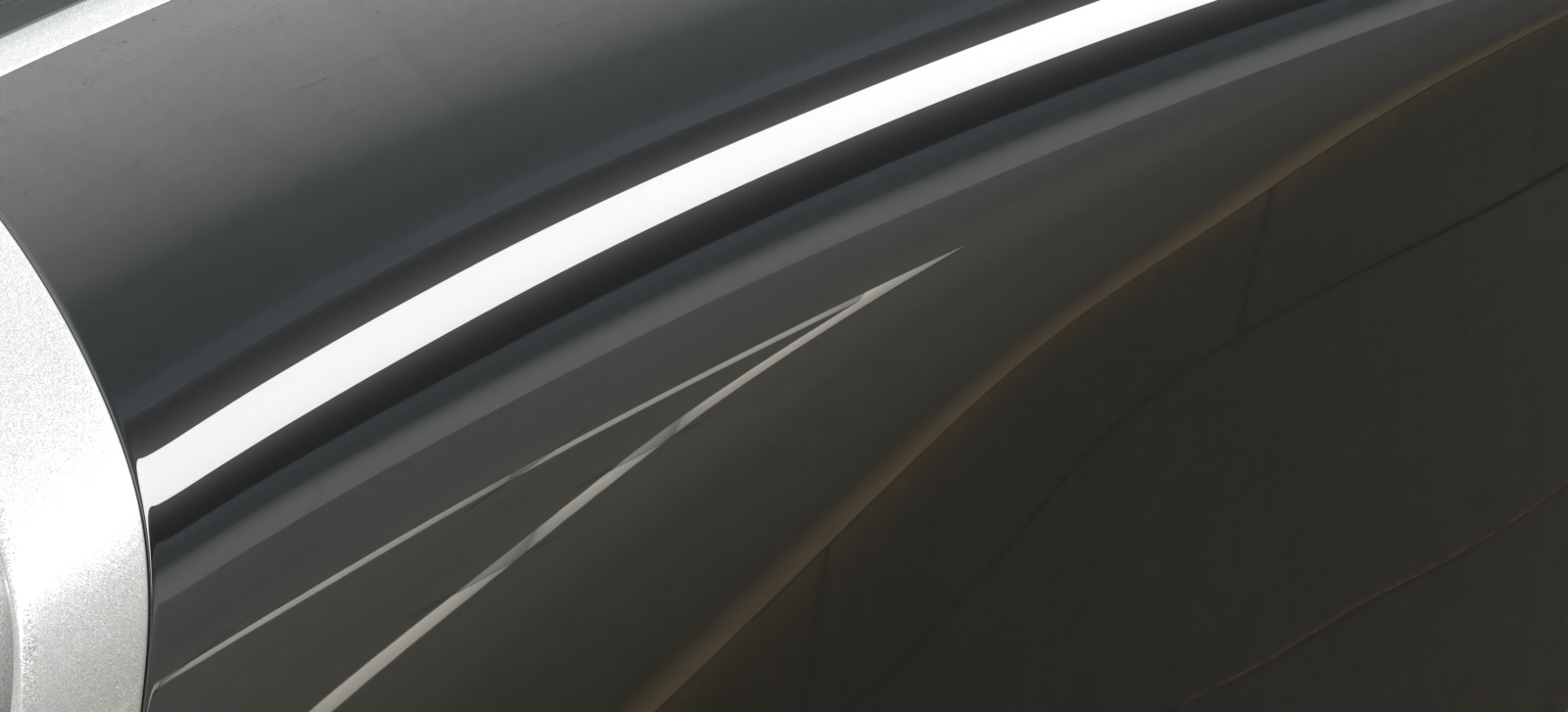
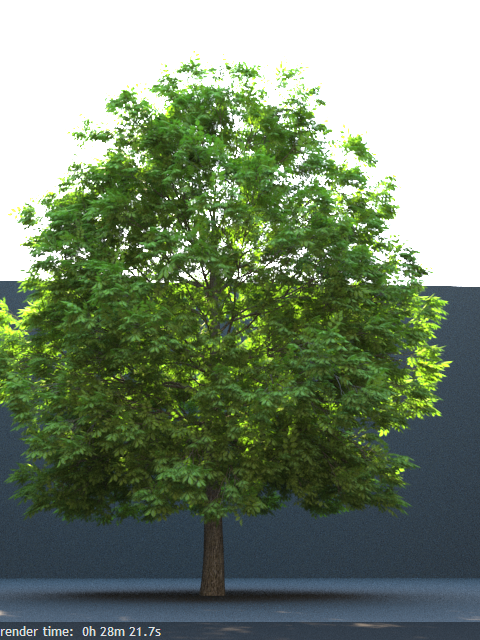
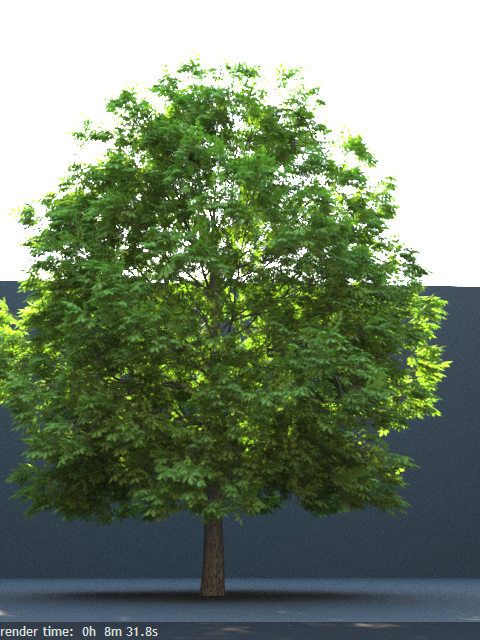
Opacity mode – Controls how opacity is sampled. For more information, see the Opacity mode parameter example below.
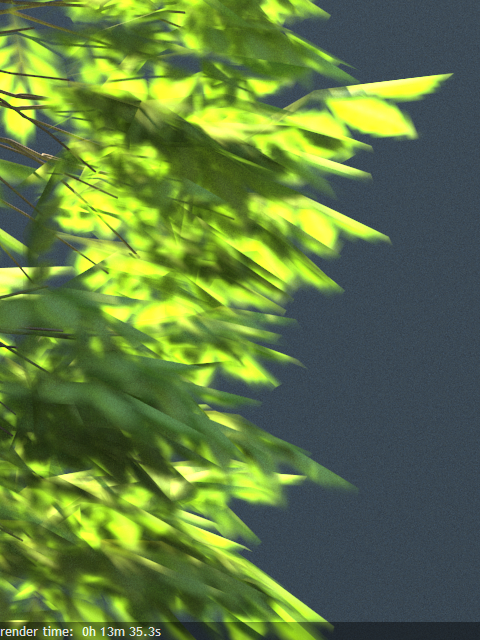
Normal – (Legacy) The opacity map is evaluated as normal: the surface lighting is computed and the ray is continued for the transparent effect. The opacity texture is filtered as normal.
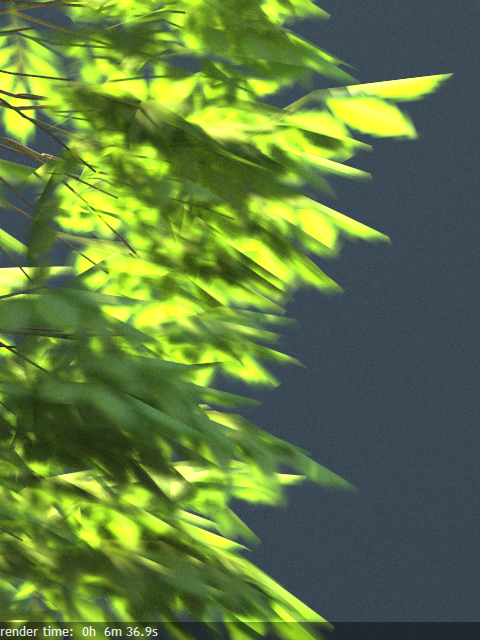
Clip – (Very fast) The opacity texture is not filtered and it is clipped to either fully opaque or fully transparent based on the mid-point value. Useful when there are many transparent surfaces one behind the other like leaves.
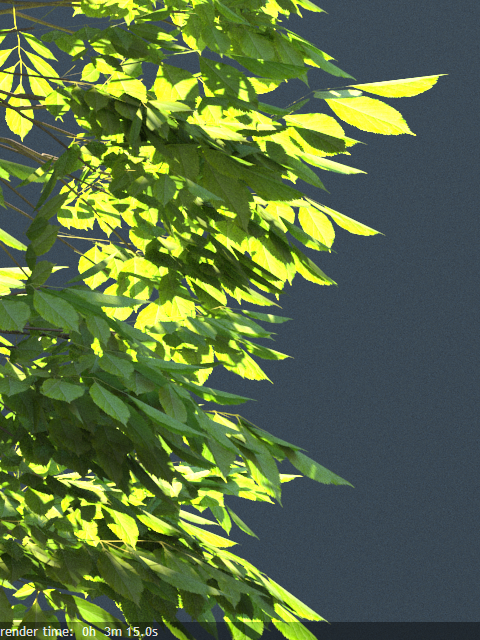
Stochastic – (Optimal) The opacity texture is filtered and the surface is randomly shaded as either fully opaque or fully transparent for a correct average appearance.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
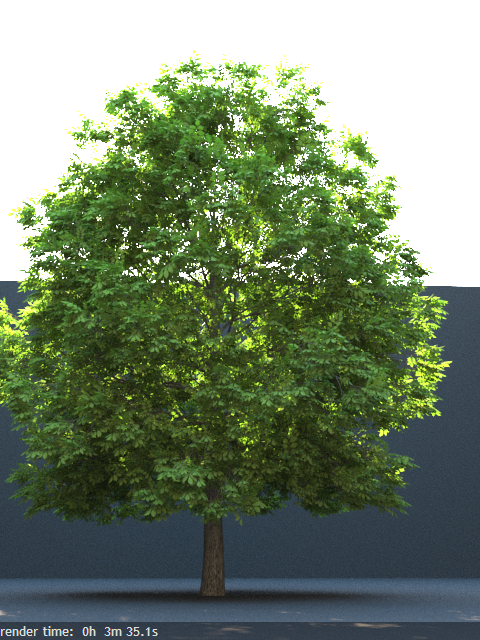
Example: Opacity mode parameter
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The renders below show a blow-up of the tree to better show the effect of the different modes. Note that in the first two renders the opacity is blurry because of the texture filtering.
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Lock Fresnel IOR To Refraction IOR – Allows you to unlock the Fresnel IOR parameter for finer control over the reflections.Fresnel IOR – The IOR to use when calculating Fresnel reflections. Normally this is locked to the Refraction IOR parameter, but you can unlock it for finer control.for finer control over the reflections.
Fresnel IOR – The IOR to use when calculating Fresnel reflections. Normally this is locked to the Refraction IOR parameter, but you can unlock it for finer control.
Metalness – Controls the reflection model of the material from dielectric (metalness 0.0) to metallic (metalness 1.0). Note that intermediate values between 0.0 and 1.0 do not correspond to any physical material. This parameter can be used with PBR setups coming from other applications. The reflection color should typically be set to white for real world materials.
Trace Reflections – Check to enable reflections for the material.
...