This page provides information on the SSS 2 Complex Node in V-Ray for Blender.
Overview
This node is the default material node. It requires that a BRDF node is connected to its input.
UI Path
||Node Editor|| > Add > BRDF > SSS 2 Complex
Node
Overall color - Controls the overall coloration for the material. This color serves as a filter for both the diffuse and the sub-surface component.
Diffuse color -The color of the diffuse portion of the material.
Diffuse amount - The amount for the diffuse component of the material. Note that this value in fact blends between the diffuse and sub-surface layers. When set to 0.0, the material does not have a diffuse component. When set to 1.0, the material has only a diffuse component, without a sub-surface layer. The diffuse layer can be used to simulate dust etc. on the surface.
Sub surface color - The general color for the sub-surface portion of the material
Scatter Radius - The internal scattering color for the material. Brighter colors cause the material to scatter more light and to appear more translucent; darker colors cause the material to look more diffuse-like.
Scatter radius Mult. - Controls the amount of light scattering in the material. Smaller values cause the material to scatter less light and to appear more diffuse-like; higher values make the material more translucent. Note that this value is specified always in centimeters (cm); the material will automatically convert it into scene units based on the currently selected system units.
Specular color - Determines the specular color for the material.
Specular amount - Determines the specular amount for the material. Note that there is an automatic Fresnel falloff applied to the specular component, based on the IOR of the material.
Specular glossiness - Determines the glossiness (highlights shape). A value of 1.0 produces sharp reflections, lower values produce more blurred reflections and highlights.
Opacity -
Parameters
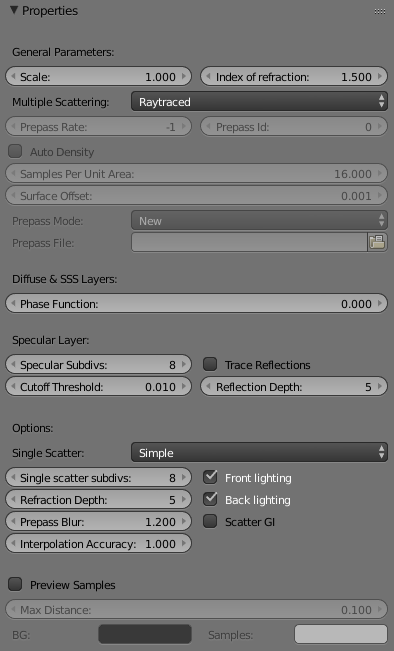
General Parameters
Scale - Scales the subsurface scattering radius additionally. Normally, VRayFastSSS2 will take the scene units into account when calculating the subsurface scattering effect. However, if the scene was not modeled to scale, this parameter can be used to adjust the effect. It can also be used to modify the effect of the presets, which reset the Scatter radius parameter when loaded, but leave the Scale parameter unchanged.
Index of refraction – Specifies the index of refraction for the material. Most water-based materials like skin have IOR of about 1.3.
Multiple Scattering – Controls the method used to calculate the subsurface scattering effect.
Raytraced – True raytracing inside the volume of the geometry is used to get the subsurface scattering effect. This method is physically accurate and produces the best results.
Prepass-based illumination map – This method uses an approach similar to the irradiance map to approximate the sub-surface scattering effect. It requires a prepass and the quality of the final result depends on the prepass rate parameter
Object-based illumination map – This method is similar to the Prepass-based illumination map in that it also creates an illumination map used to approximate the final result. The only difference is the method used for sample placement. Rather than using the resolution of the image as a guide, the samples are placed based on the surface area of the geometry. When this mode is used, the final quality depends on the samples per unit area parameter.
Prepass
V-Ray uses a pre-pass similar to the Irradiance Map in order to generate the SSS effect. These parameters allow you to set up the pre-pass.
Rate – Accelerates the calculation of multiple scattering by precomputing the lighting at different points on the surface of the object and storing them in a structure called an illumination map, which is similar to the irradiance map used to approximate global illumination, and uses the same prepass mechanism built into V-Ray that is also used for interpolated glossy reflections/refractions. This parameter determines the resolution at which surface lighting is computed during the prepass phase. A value of 0 means that the prepass will be at the final image resolution; a value of -1 means half the image resolution, and so on. For high quality renders it is recommended to set this to 0 or higher, as lower values may cause artifacts or flickering in animations. If the chosen prepass rate is not sufficient to approximate the multiple scattering effect adequately, SSS 2 will replace it with a simple diffuse term. This can happen, for example, for objects that are very far away from the camera, or if the subsurface scattering effect is very small. This simplification is controlled by the Blur parameter.
ID – This option allows several SSS2 materials to share the same illumination map. This could be useful if you have different SSS2 materials applied on the same object. If this is greater than 0, then all materials with the specified ID will share the same map.
Auto density – When this option is enabled V-Ray automatically assigns the number of samples to be used for each square unit of surface on the geometry. Enabling this check box disables the Samples per unit area parameter.
Samples per unit area – Has effect only when the Auto calculate density check box is disabled. It allows you to control the number of samples that are going to be taken for each square unit of the geometry surface. The size of one unit is controlled by the 3ds Max scene units set up. Increasing this parameter means that more samples are going to be taken which produces higher quality results at the cost of increased render times.
Surface offset – To prevent artifacts, each sample is taken a tiny distance away from the actual surface in the direction of the normal. This parameter controls that offset.
Mode – Allows the user to select the way the illumination map (prepass) is (re)used.
New – When this mode is enabled, V-Ray will calculate a new illumination map for each rendering.
Save (Per-Frame) – When this mode is enabled V-Ray will calculate a new illumination map and save it in a file specified in prepass fileName.
Load (Per-Frame) – When this mode is enabled V-Ray is not going to calculate a new illumination map. Instead it will use the map specified in prepass fileName to render the image.
File - Specifies the file name of the illumination map to be saved in or read from.
Diffuse & SSS Layers
Phase function - Determines the general way light scatters inside the material through a value between -1.0 and 1.0. Its effect can be somewhat likened to the difference between diffuse and glossy reflections from a surface, however the phase function controls the reflection and transmittance of a volume. A value of 0.0 means that light scatters uniformly in all directions (isotropic scattering); positive values mean that light scatters predominantly forward in the same direction as it comes from; negative values mean that light scatters mostly backward. Most water-based materials (e.g. skin, milk) exhibit strong forward scattering, while hard materials like marble exhibit backward scattering. This parameter affects most strongly the single scattering component of the material. Positive values reduce the visible effect of single scattering component, while negative values make the single scattering component generally more prominent.
Specular Layer
Specular Subdivs - Determines the number of samples that will be used to calculate glossy reflections. Lower values render faster, but may produce noise in the glossy reflections. Higher values reduce the noise, but may be slower to calculate.
Cutoff Threshold - Specifies a threshold below which reflections/refractions will not be traced. V-Ray tries to estimate the contribution of reflections/refractions to the image, and if it is below this threshold, these effects are not computed. Do not set this to 0.0 as it may cause excessively long render times in some cases.
Trace Reflections - Enables or disables the tracing of specular reflections.
Reflection depth - Allows you to set an upper limit to the number of times a ray of light will be reflected or refracted in the object.
Options
Single Scatter - Controls how the single scattering component is calculated.
None – No single scattering component is calculated.
Simple – The single scattering component is approximated from the surface lighting. This option is useful for relatively opaque materials like skin, where light penetration is normally limited.
Raytraced (solid) – The single scattering component is accurately calculated by sampling the volume inside the object. Only the volume is raytraced; no refraction rays on the other side of the object are traced. This is useful for highly translucent materials like marble or milk, which at the same time are relatively opaque.
Raytraced (refractive) – Similar to the Raytraced (solid) mode, but refraction rays are traced as well. This option is useful for transparent materials like water or glass. In this mode, the material will also produce transparent shadows.
Single scatter subdivs – Determines the number of samples to take when evaluating the single scattering component when the single scatter mode is set to Raytraced (solid) or Raytraced (refractive).
Refraction Depth – Determines the depth of refraction rays when the single scatter parameter is set to Raytraced (refractive) mode.
Prepass Blur - Determines if the material will use a simplified diffuse version of the multiple scattering when the prepass rate for the direct lighting map is too low to adequately approximate it. A value of 0.0 will cause the material to always use the illumination map. However, for objects that are far away from the camera, this may lead to artifacts or flickering in animations. Larger values control the minimum required samples from the illumination map in order to use it for approximating multiple scattering.
Interpolation Accuracy – Controls the quality of the approximation of the multiple scattering effect when the type is Prepass-based illumination map or Object-based illumination map. Larger values produce more accurate results but are slower to render. Lower values render faster, but too low values may produce blocky artifacts on the surface.
Front lighting – Enables the multiple scattering component for light that falls on the same side of the object as the camera.
Back lighting – Enables the multiple scattering component for light that falls on the opposite side of the object as the camera. If the material is relatively opaque, turning this off will speed up the rendering.
Scatter GI – Controls whether the material will accurately scatter global illumination. When disabled, the global illumination is calculated using a simple diffuse approximation on top of the sub-surface scattering. When enabled, the global illumination is included as part of the surface illumination map for multiple scattering. This is more accurate, especially for highly translucent materials, but may slow down the rendering quite a bit.
Preview samples - When this option is enabled, V-Ray renders an image that displays the samples distribution along the surface of the geometry. It can be used for debugging artifacts much like the show samples parameter of the Irradiance Map.
Max distance - Each sample is represented by a circle in the final image. This parameter allows the user to specify the radius of the sample.
BG - The background color of the geometry where no samples are present.
Samples - The color of the samples.